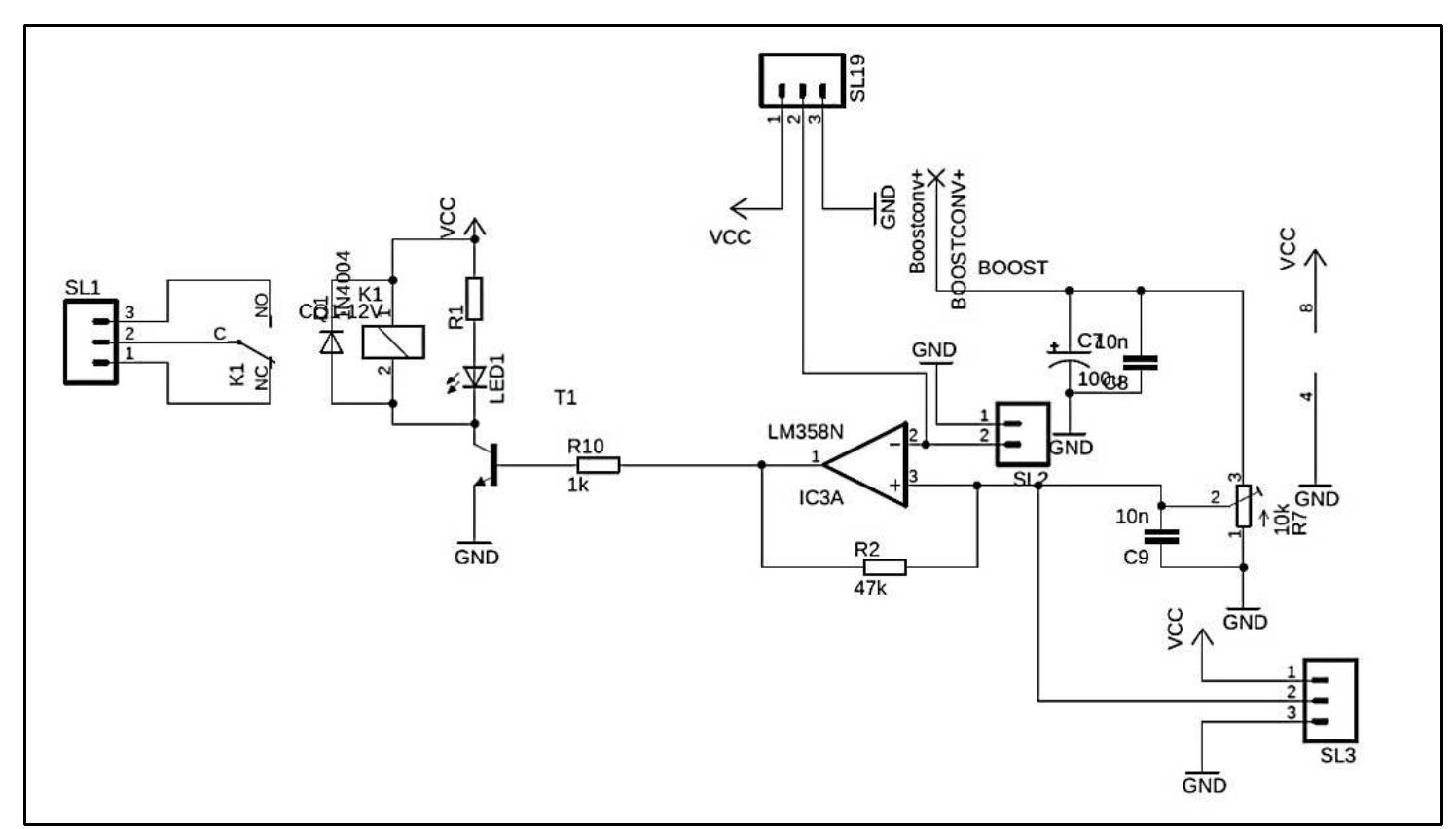
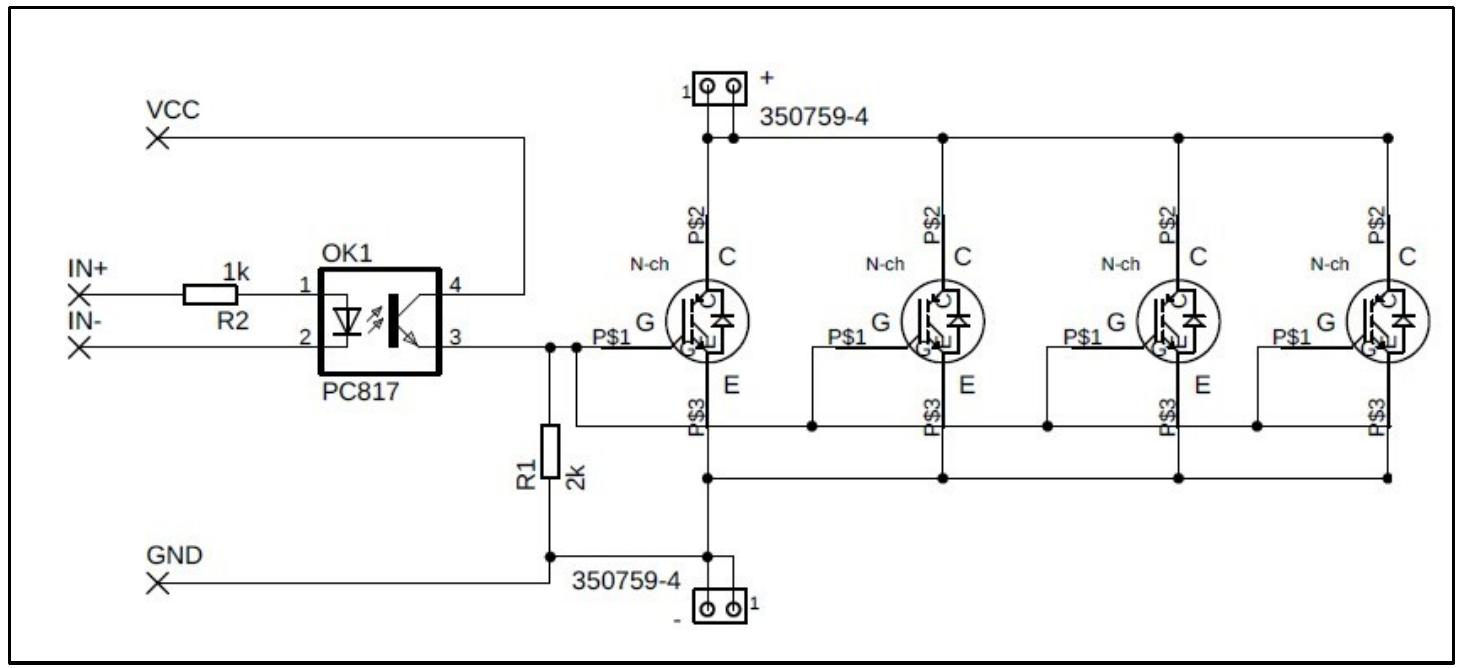
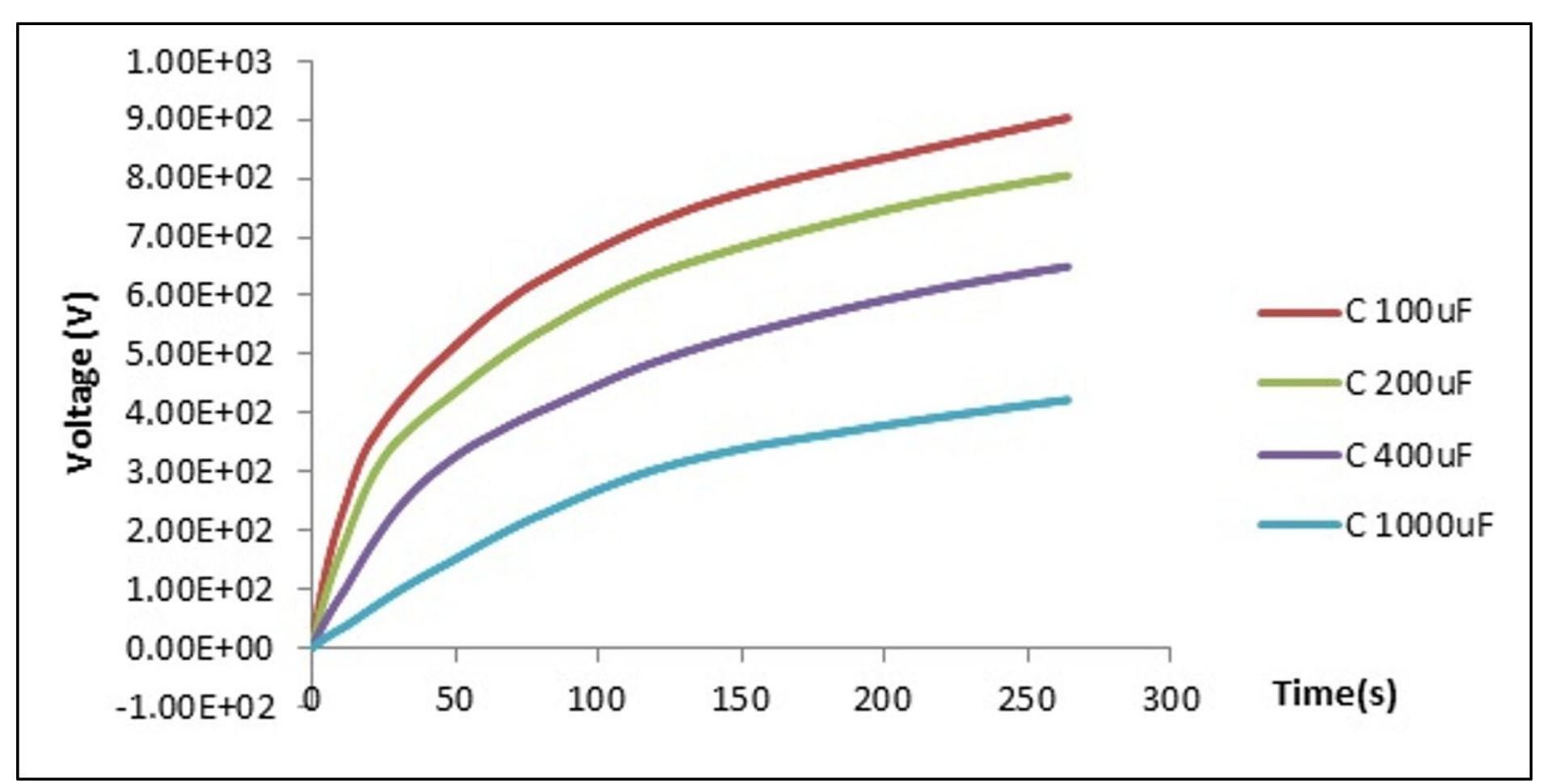
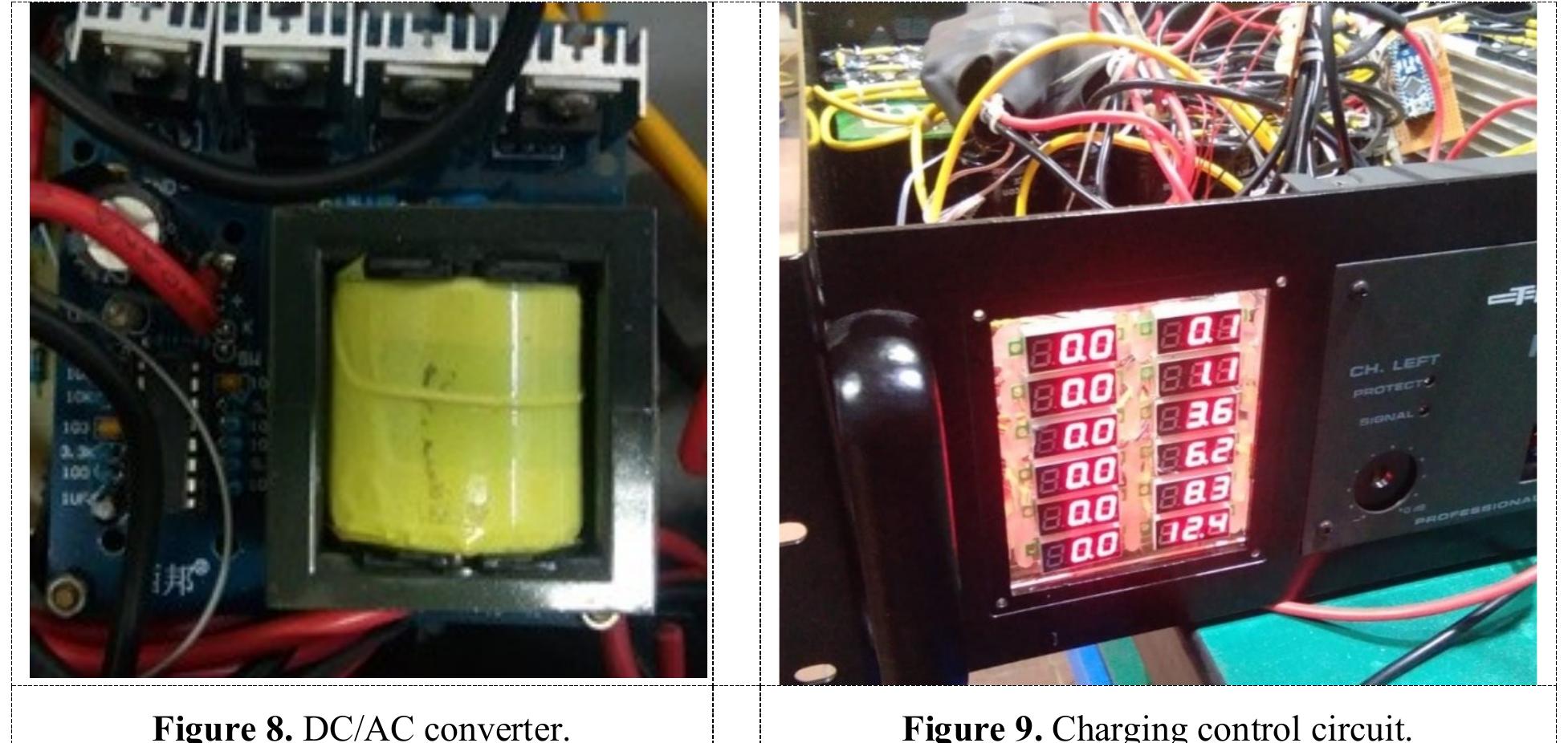
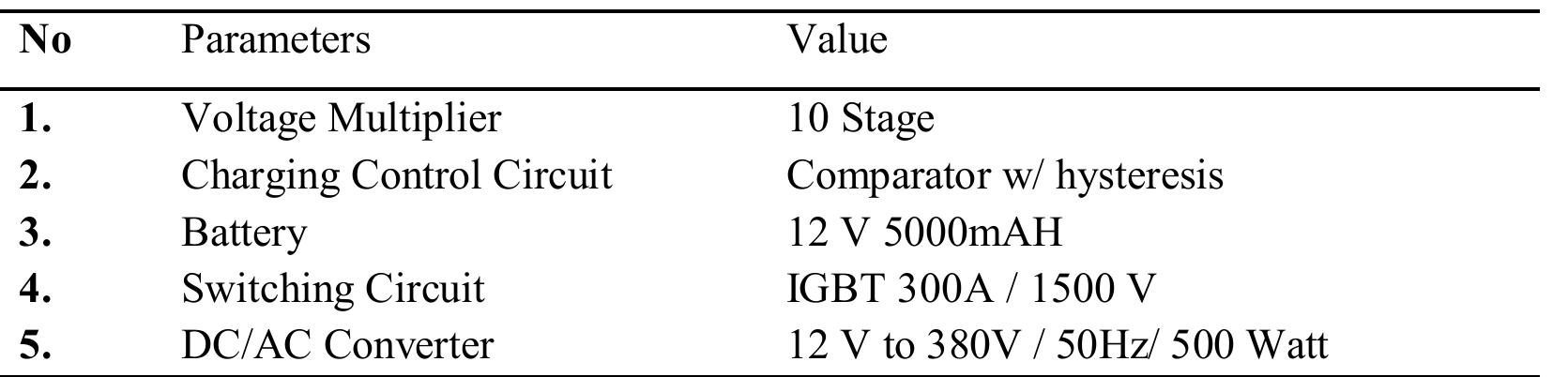
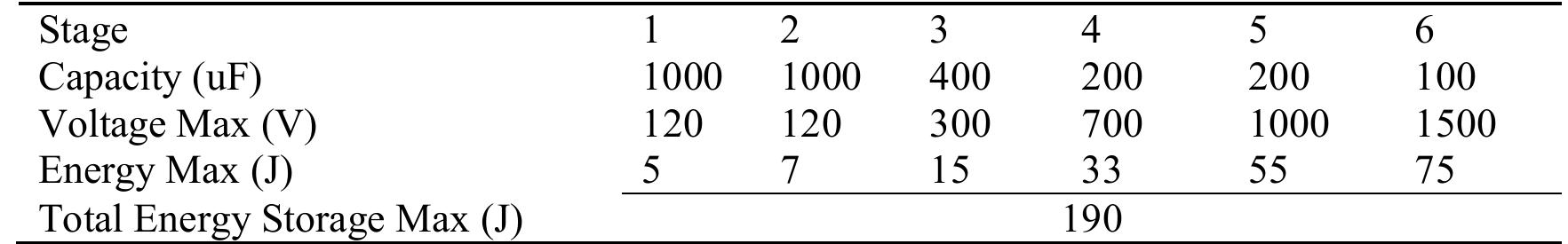
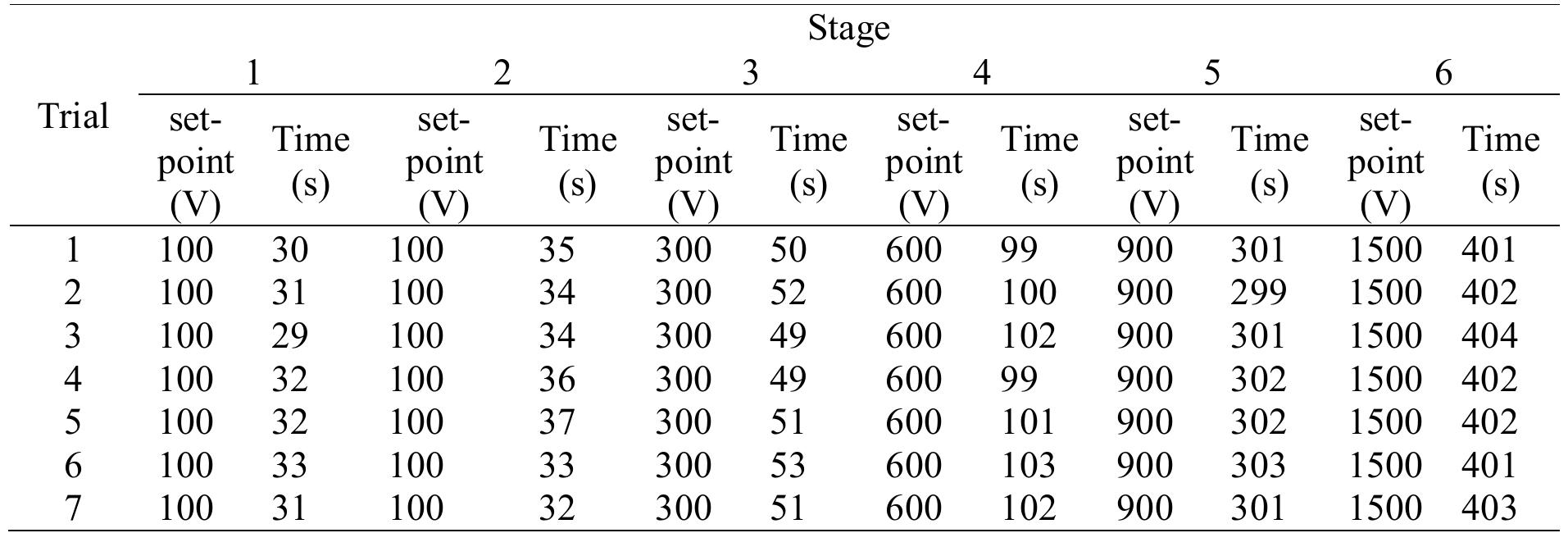
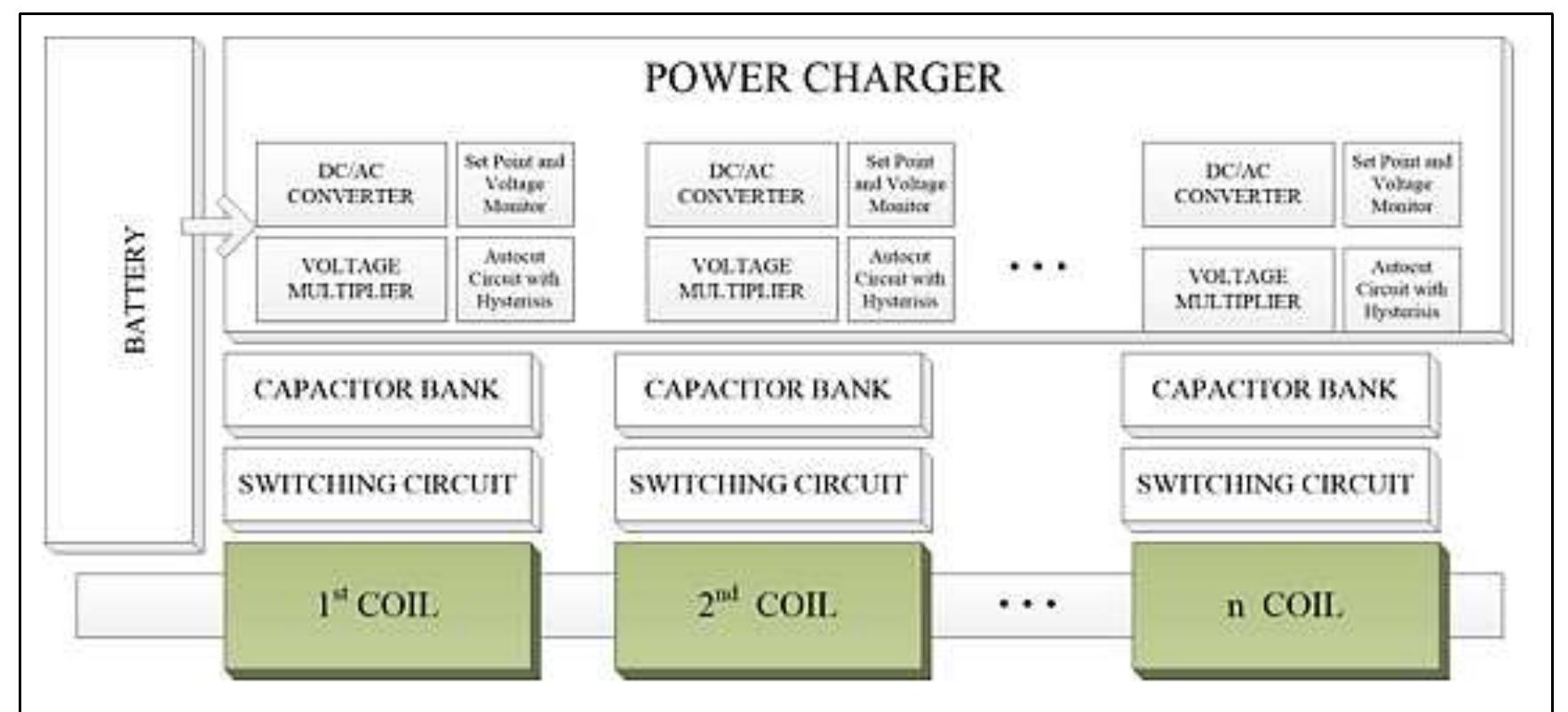
Key research themes
1. How do explosive electrical discharges in conductors generate shock waves and drive detonation processes?
This research area focuses on understanding the mechanisms by which rapid electrical energy deposition into conductors results in explosive vaporization and plasma formation, which subsequently generates strong shock waves. These shock waves can initiate detonation of surrounding explosives or cause material deformation. This understanding is critical for designing controlled detonators, explosive welding, or material processing using electrically exploded conductors. Key issues include the influence of wire material and geometry, energy deposition rates, and environmental conditions such as underwater or vacuum.
2. What are the underlying electrodynamic forces and transient processes driving conductor fragmentation under high-power current pulses?
This theme investigates the fundamental physics of conductor fragmentation during rapid current pulses, focusing on transient electromagnetic forces inside metallic lattices. It clarifies how radiation-induced dipole-dipole interactions create strong bipolar tensile forces that can exceed material strength, leading to fragmentation or fatigue. Understanding these forces aids in designing pulsed power systems and novel applications such as solid-state ion colliders or enhanced electrical explosion control.
3. How can exploding conductors be used to study non-ideal detonation initiation and related explosive phenomena?
This theme covers the use of electrically exploded wires and conductors as initiators or experimental platforms for studying detonation initiation, propagation, and explosive behavior of heterogeneous energetic materials. It includes investigations on parameters influencing non-ideal explosive behavior such as ANFO and the coupling between electrical explosion and subsequent explosive shock initiation. These studies enhance the understanding of initiation mechanisms crucial for safe and efficient explosive device design and forensic analysis.