Version 1.107 is now available! Read about the new features and fixes from November.
Dismiss this update
You can use Docker with the Dev Containers extension in a few ways:
Continue reading to learn alternate ways you can install and use Docker or a Docker compliant CLI.
On Windows, you can use Docker installed in WSL through the WSL extension. You can reference the Docker documentation for installing Docker on Linux, with specific information per distribution.
One issue is that the dockerd daemon won't start automatically due to the lack of systemd or any other system daemon. In WSL version 0.67.6 and later (wsl --version), you can enable support for systemd. With older WSL versions, you can use Distrod to create or update existing WSL distros with systemd.
Colima provides container runtimes on macOS. It's recommended to use Colima v0.2.2 or later so that VS Code can properly see containers running through Colima.
Colima automatically sets up a colima Docker context and makes it the active context. You may also want to install the docker and docker-compose CLIs before running colima start for this setup to work properly.
Note: Colima uses Alpine Linux, which isn't supported by Remote - SSH.
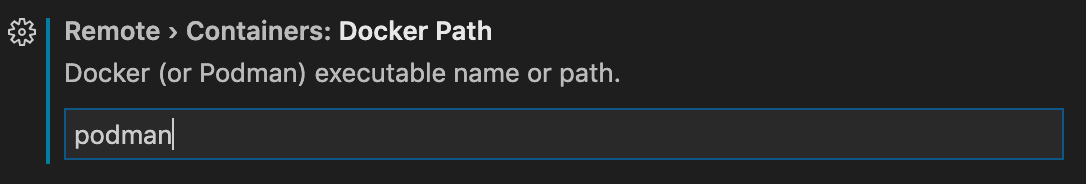
Podman version 5+ is mostly compatible with Docker's CLI commands. To use Podman, update the Docker Path (dev.containers.dockerPath) setting to podman on Linux, Windows, or macOS.
Podman has a podman compose command too, but that requires a compose provider that can be either Docker Compose or Podman Compose.
If you're using Linux on your local machine, or already have a remote Linux machine with SSH access, you can reference the Docker documentation for installing Docker on Linux, with specific information per distribution.
You can use the Remote - SSH extension with Dev Containers. This enables you to have Docker installed on your remote machine, such as a Linux VM.
You may use a Cloud-Init file (which is an industry standard) to install Docker on the VM automatically. As an example, you can create an Azure VM through the Azure CLI, and set it to use a cloud-init.txt during creation.
cloud-init.txt file:
#cloud-config
apt:
sources:
docker.list:
source: deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $RELEASE stable
keyid: 9DC858229FC7DD38854AE2D88D81803C0EBFCD88
packages:
- docker-ce
- docker-ce-cli
groups:
- docker
system_info:
default_user:
groups: [docker]
Here is an example of the Azure CLI commands. Be sure to update <location-here> to a data center close to you (for example, eastus, westeurope):
az login
az group create --name dev-server --location <location-here>
az vm create \
--resource-group dev-server \
--name dev-server \
--image Canonical:0001-com-ubuntu-server-impish:21_10-gen2:latest \
--custom-data cloud-init.txt \
--generate-ssh-keys
You can learn more about using Remote - SSH with Dev Containers in the develop on a remote Docker host documentation.
You can open or review requests for support for other container engines through the vscode-remote-release repository. There are already several feature requests you can explore: