Join a VS Code Dev Days event near you to learn about AI-assisted development in VS Code.
Dismiss this update
Agent Builder was previously known as Prompt Builder. The updated name better reflects the feature's capabilities and its focus on building agents.
Agent Builder in AI Toolkit streamlines the engineering workflow for building agents, including prompt engineering and integration with tools, such as MCP servers. It helps with common prompt engineering tasks:
Agent Builder also enhances intelligent app's capabilities with tool use:
To access Agent Builder, use either of these options:
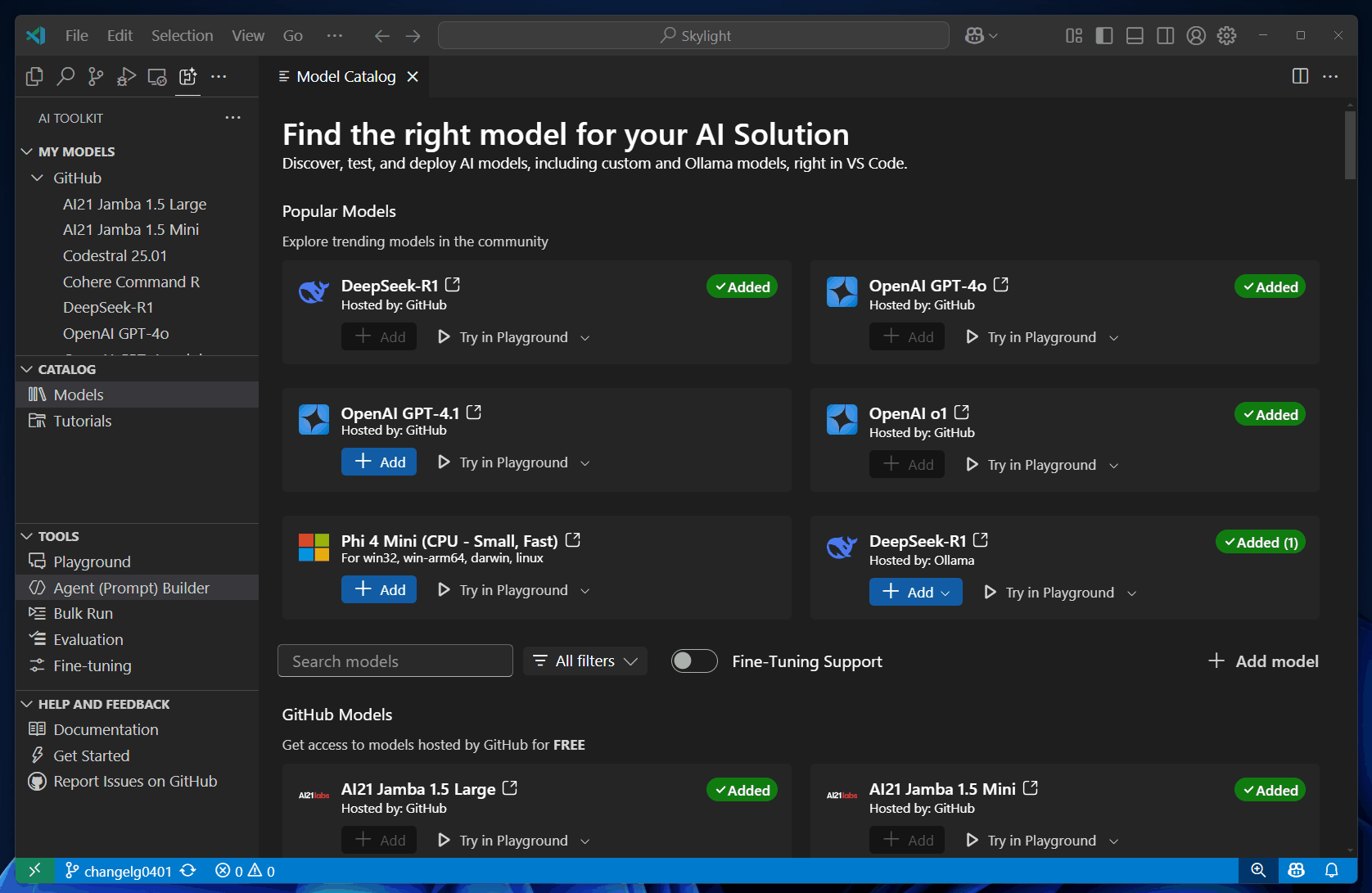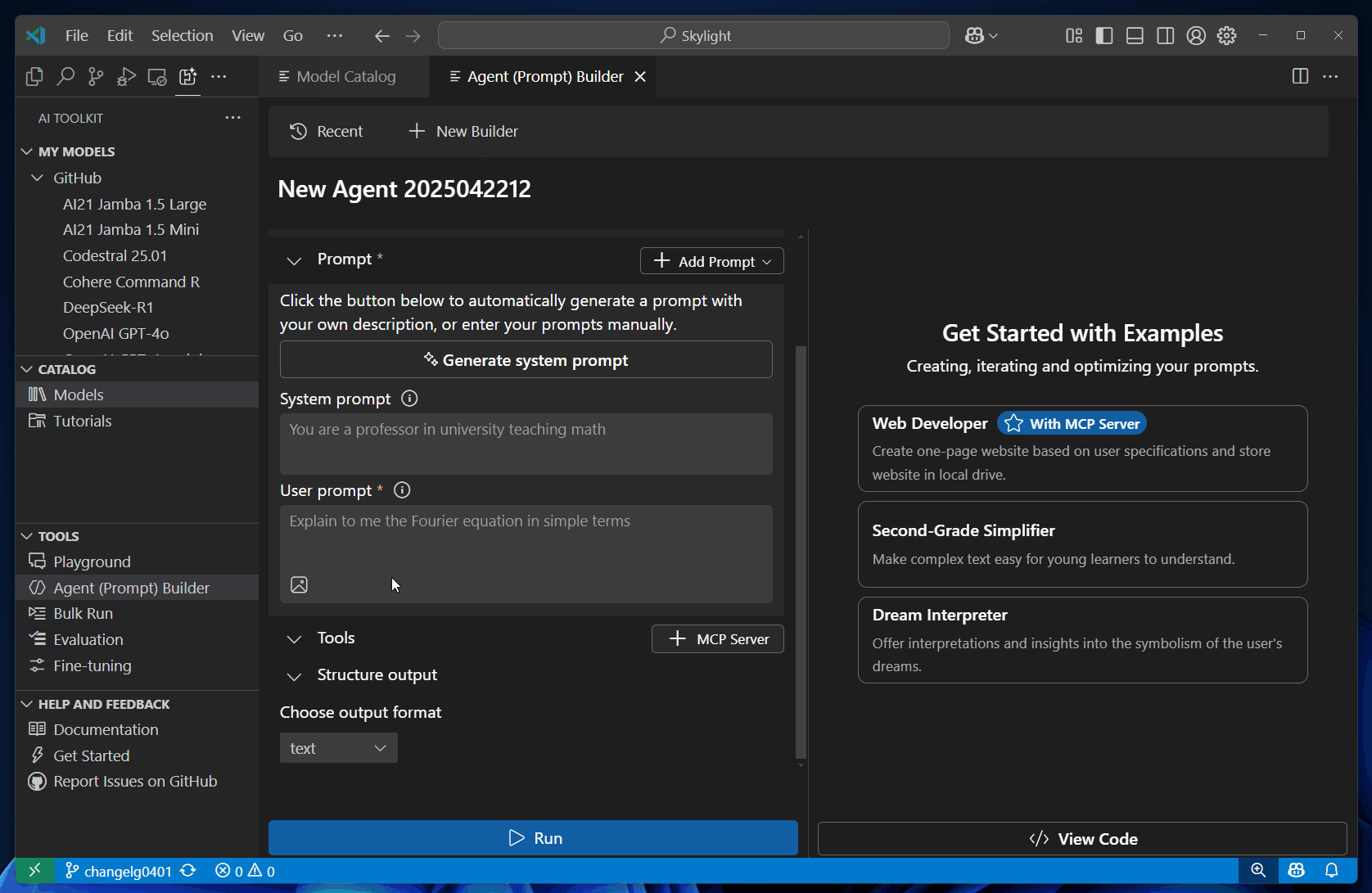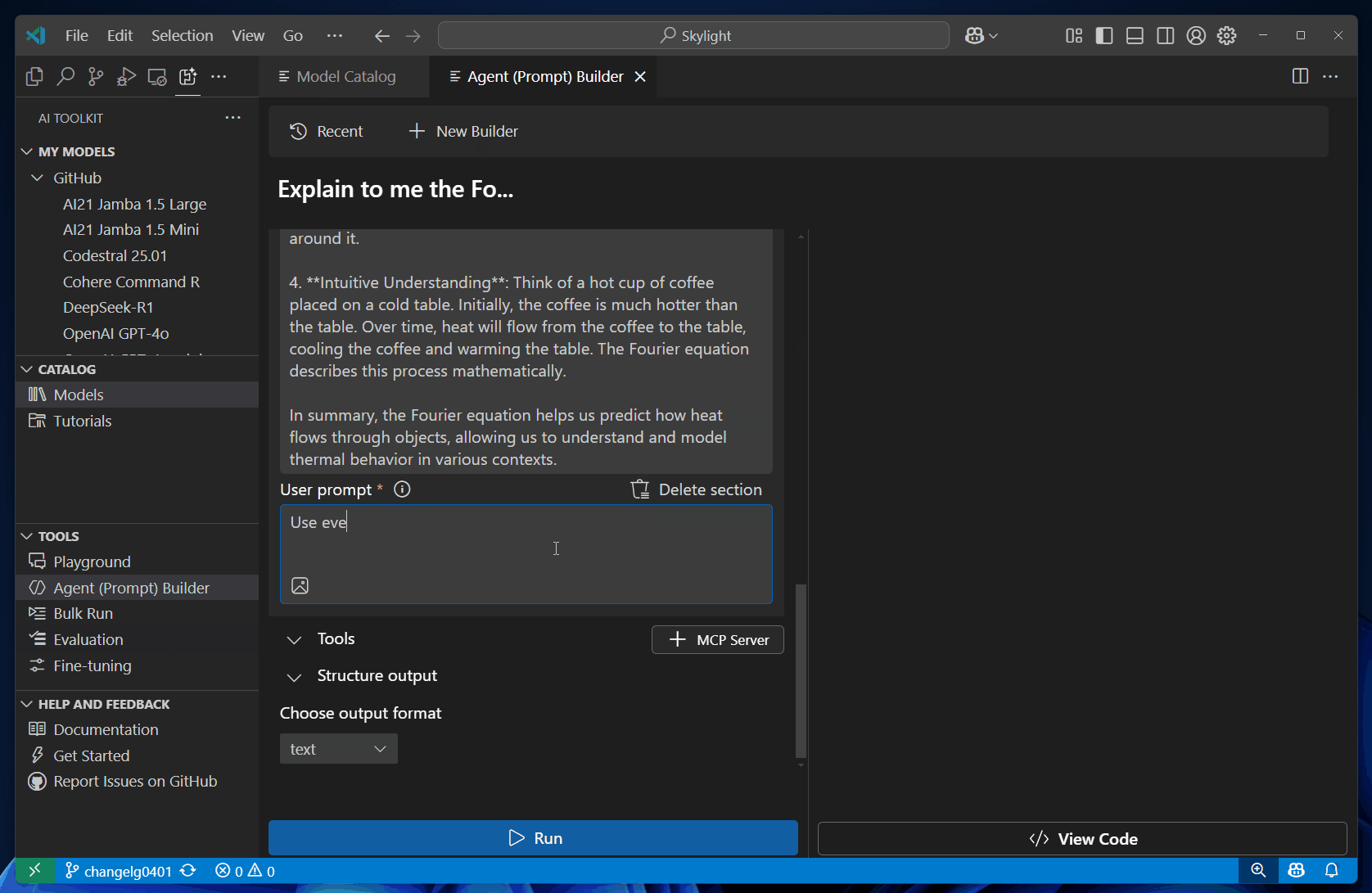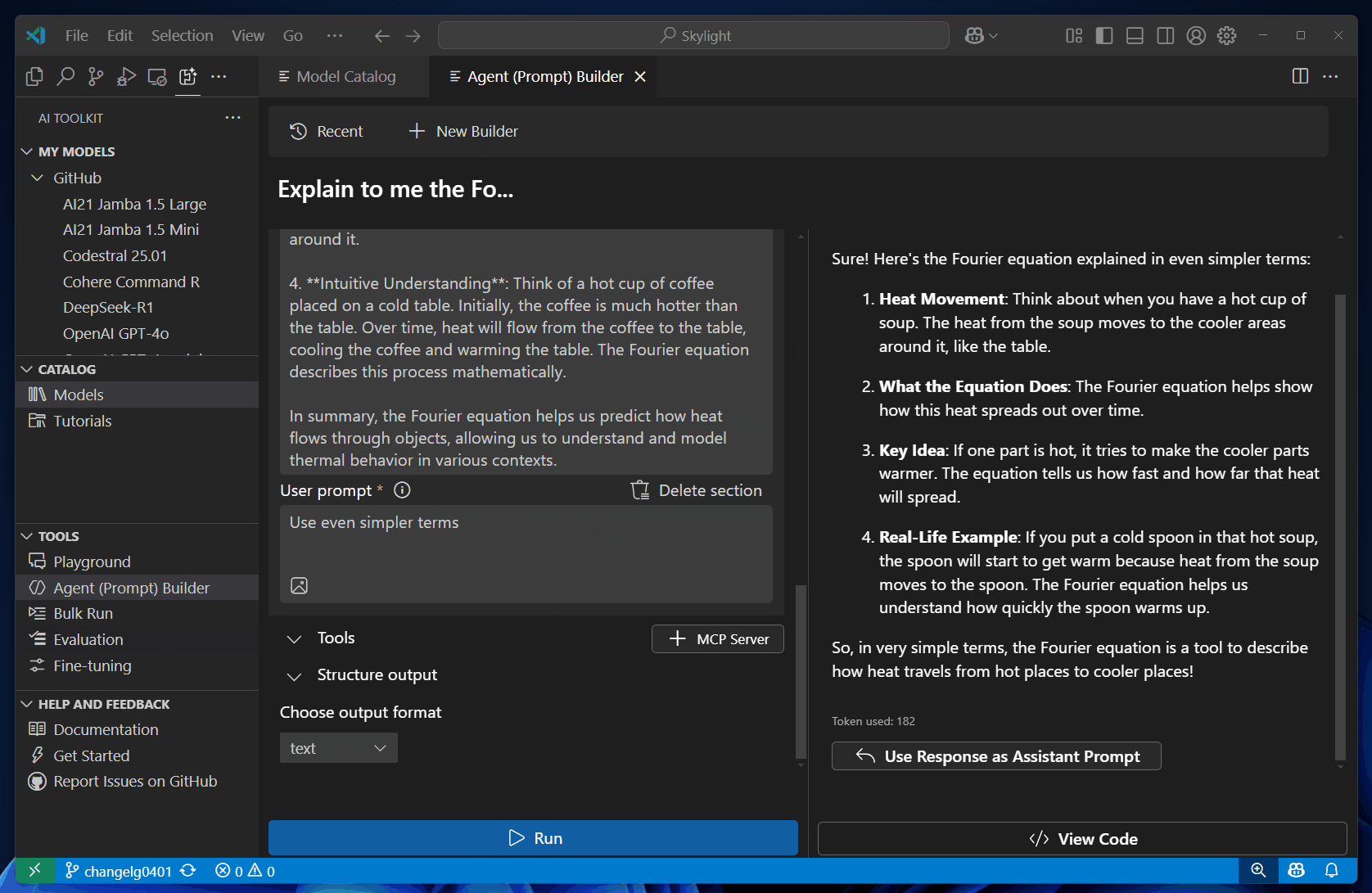
To test a prompt in Agent Builder, follow these steps:
In Models, select a model from the dropdown list, or select Browse models to add another model from the model catalog.
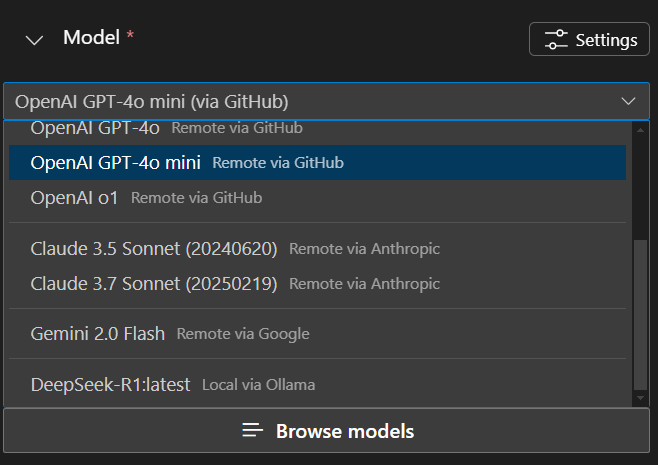
Enter a User prompt and optionally enter a System prompt.
The user prompt is the input that you want to send to the model. The optional system prompt is used to provide instructions with relevant context to guide the model response.
Describe your project idea using natural language to generate prompts automatically.
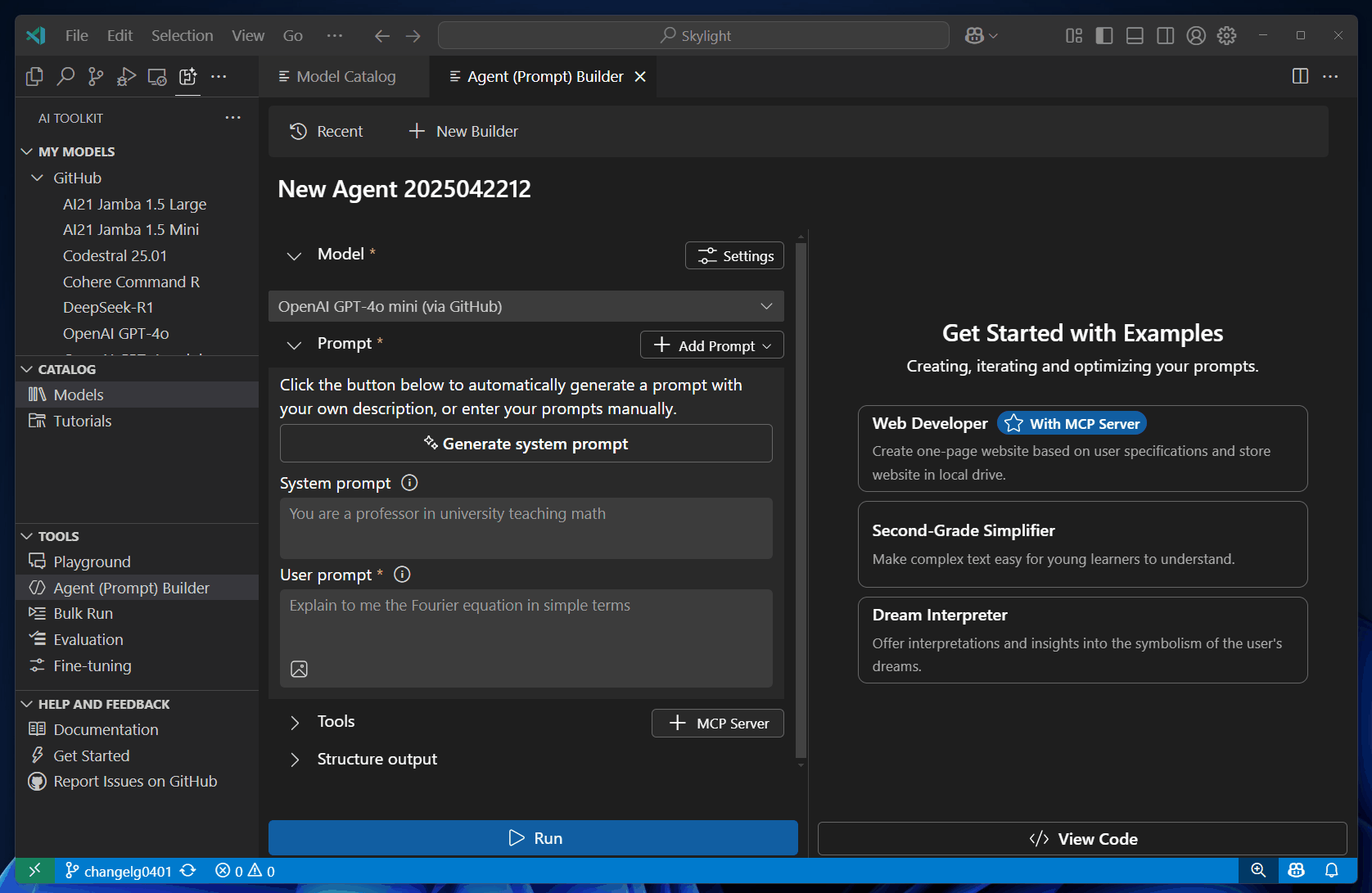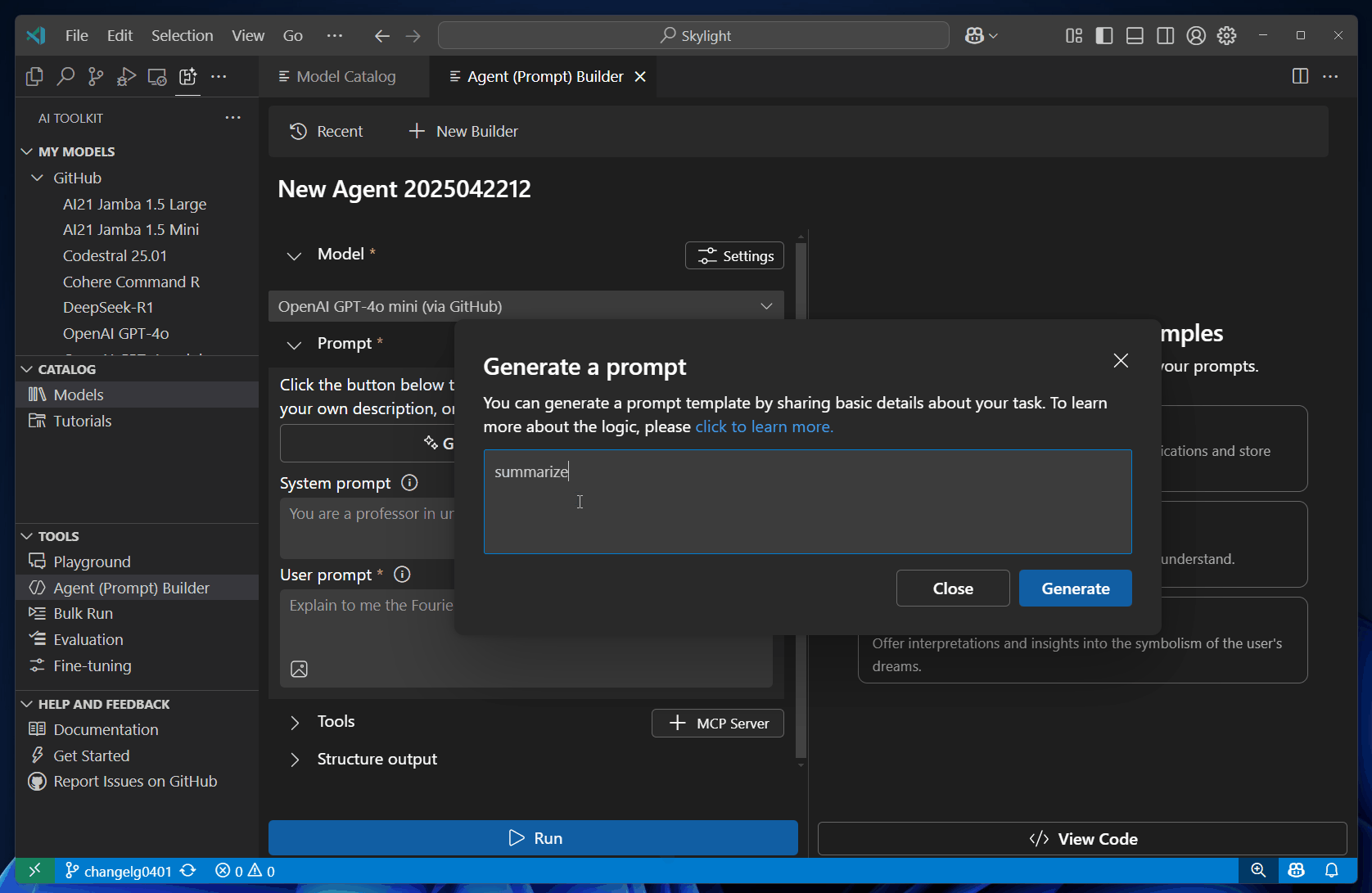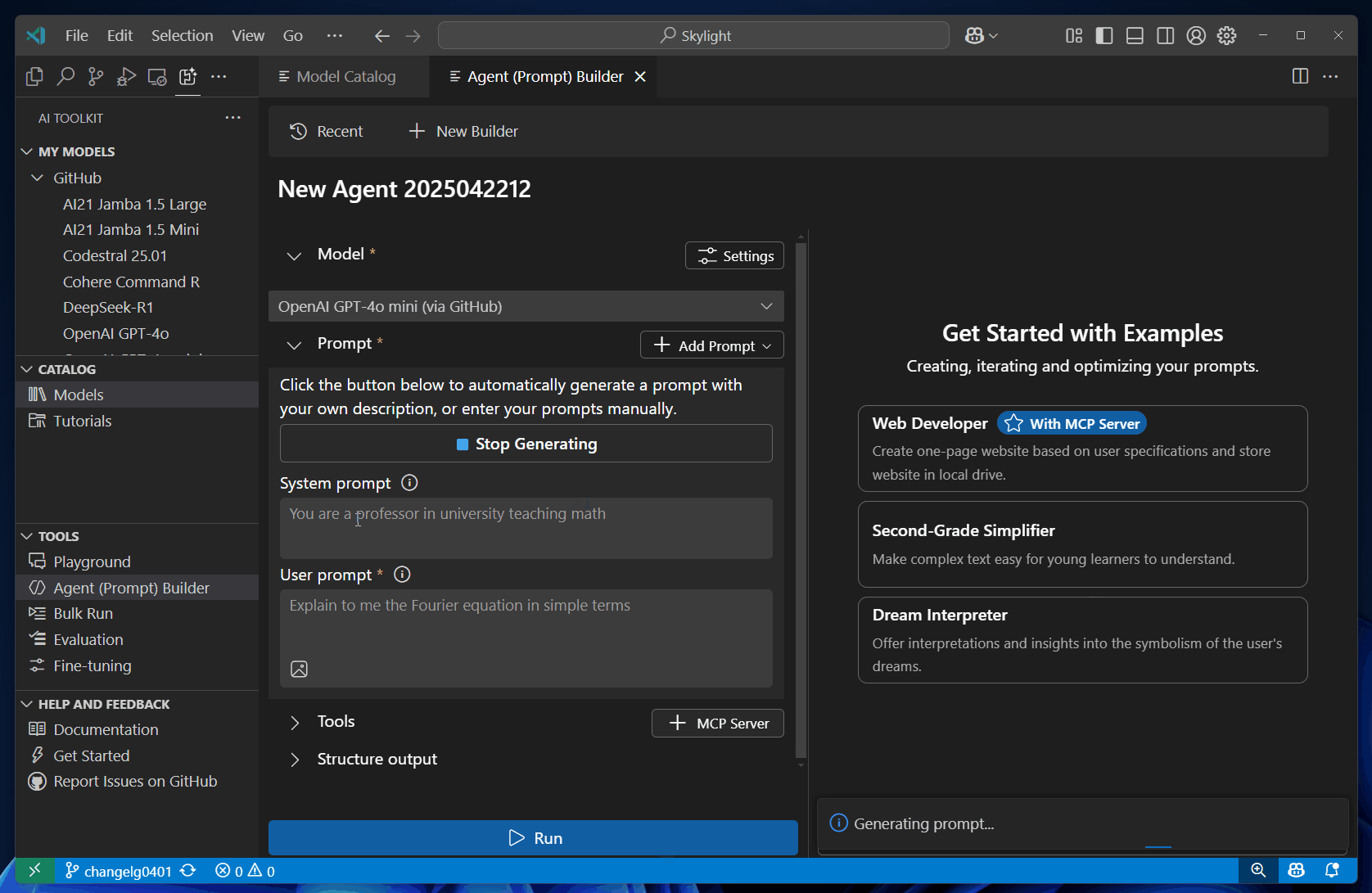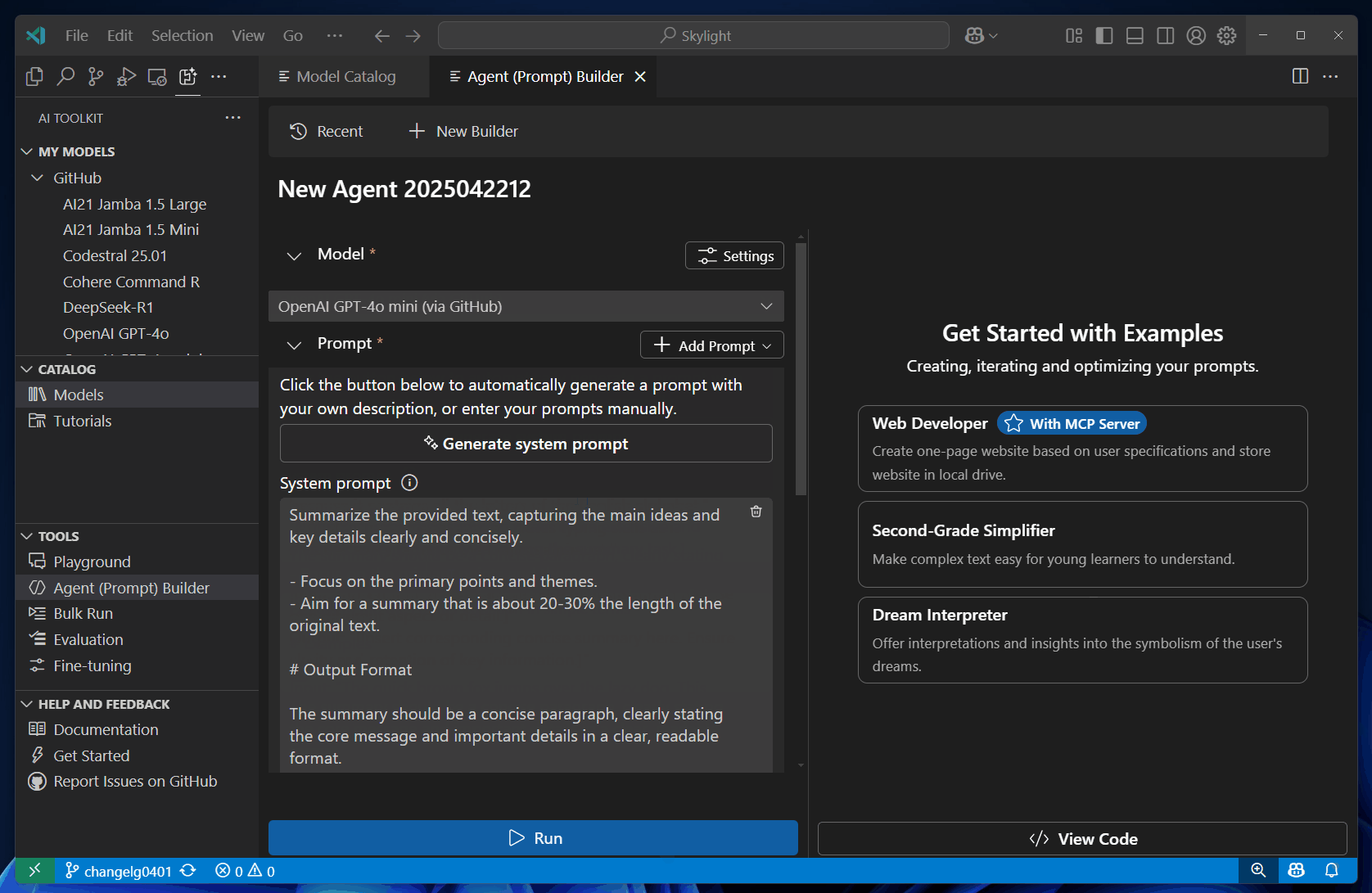
Select Run to send the prompts to the model.
Optionally, select Add Prompt to add more prompts or Add to Prompts to build conversation history.
Repeat the previous steps to iterate over your prompts by observing the model response and making changes to the prompts.
MCP server is a tool that allows you to connect to external APIs and services, enabling your agent to perform actions beyond just generating text. For example, you can use an MCP server to access databases, call web services, or interact with other applications.
Use the agent builder to discover and configure featured MCP servers, connect to existing MCP servers, or build a new MCP server from scaffold.
Using MCP servers might require either Node or Python environment. AI Toolkit validates your environment to ensure that the required dependencies are installed.
After installing, use the command npm install -g npx to install npx. If you prefer Python, we recommend using uv
AI Toolkit provides a list of featured MCP servers that you can use to connect to external APIs and services.
To configure an MCP server from featured selections, follow these steps:
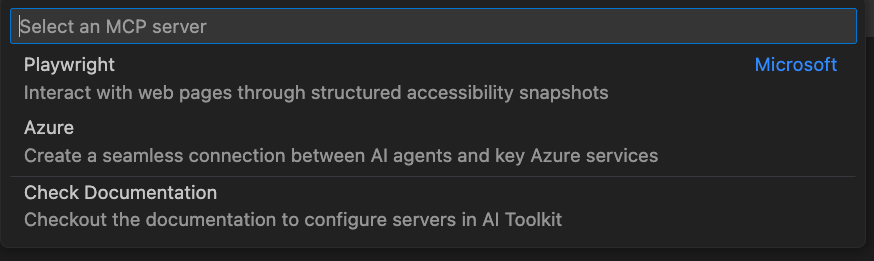
Find MCP servers in these reference servers.
To use an existing MCP server, follow these steps:
Here's an example of configuring the Filesystem server in AI Toolkit:
In the Tools section, select + MCP Server, and then select + Add server in the Quick Pick.
Select Connect to an Existing MCP Server
Select Command (stdio)
Some servers use the Python runtime and the uvx command. The process is the same as using the npx command.
Navigate to the Server instructions and locate the npx section.
Copy the command and args into the input box in AI Toolkit. For the Filesystem server example, it's npx -y @modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem /Users/<username>/.aitk/examples
Input a name for the server.
Optionally, enter extra environment variables.
Some servers might require extra environment variables such as API keys. In this case, AI Toolkit fails at the stage of adding tools and a file mcp.json opens, where you can enter the required server details following the instructions provided by each server.
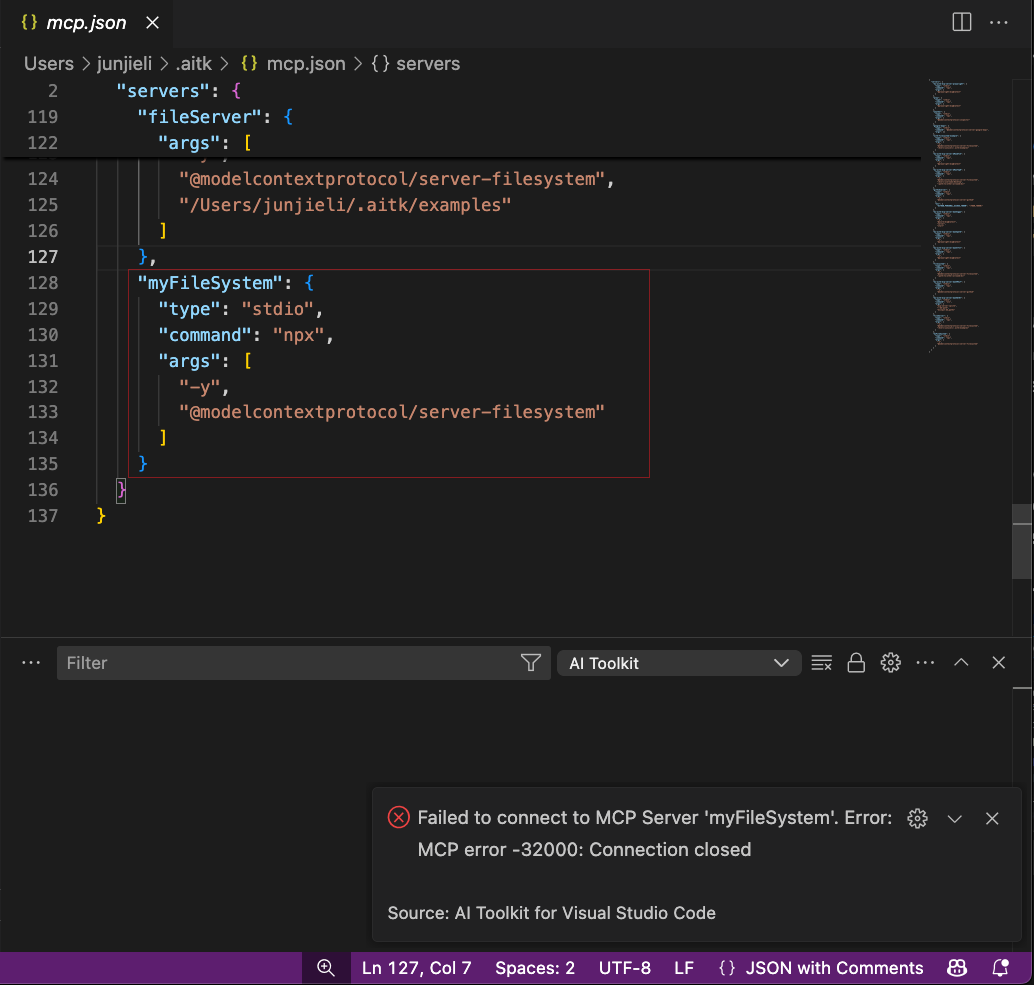 After you complete the configuration:
1. Navigate back to Tools section and select + MCP Server
1. Select the server you configured from the dropdown list
After you complete the configuration:
1. Navigate back to Tools section and select + MCP Server
1. Select the server you configured from the dropdown list
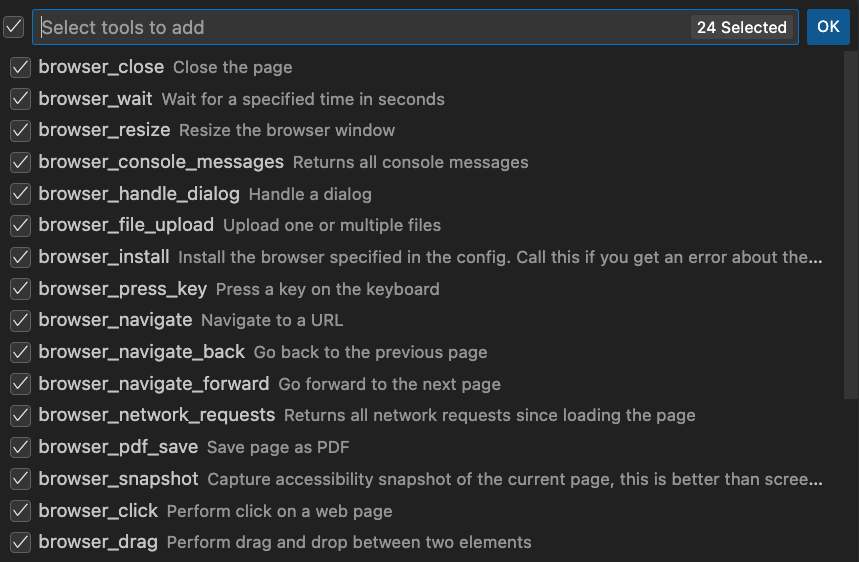
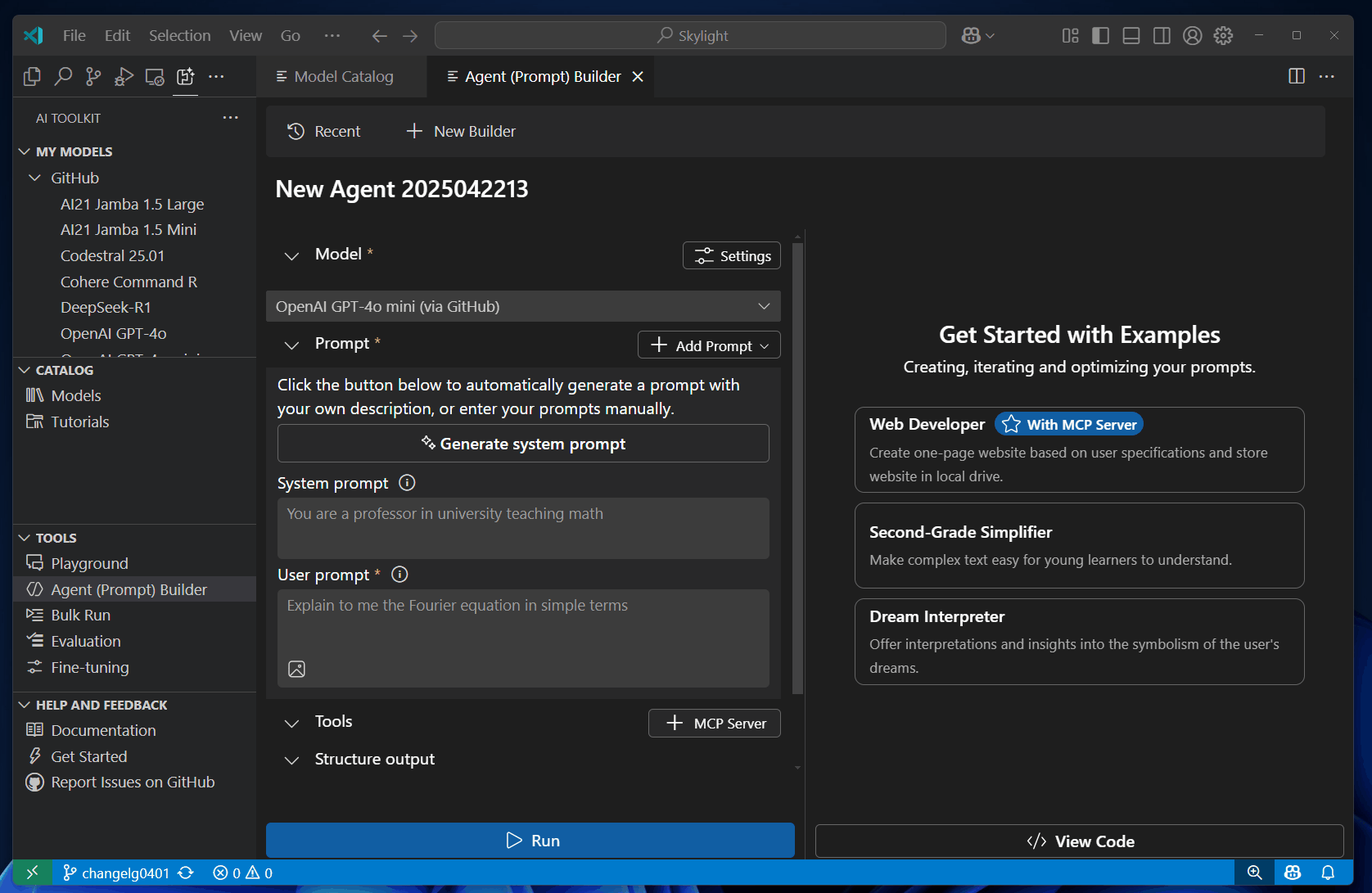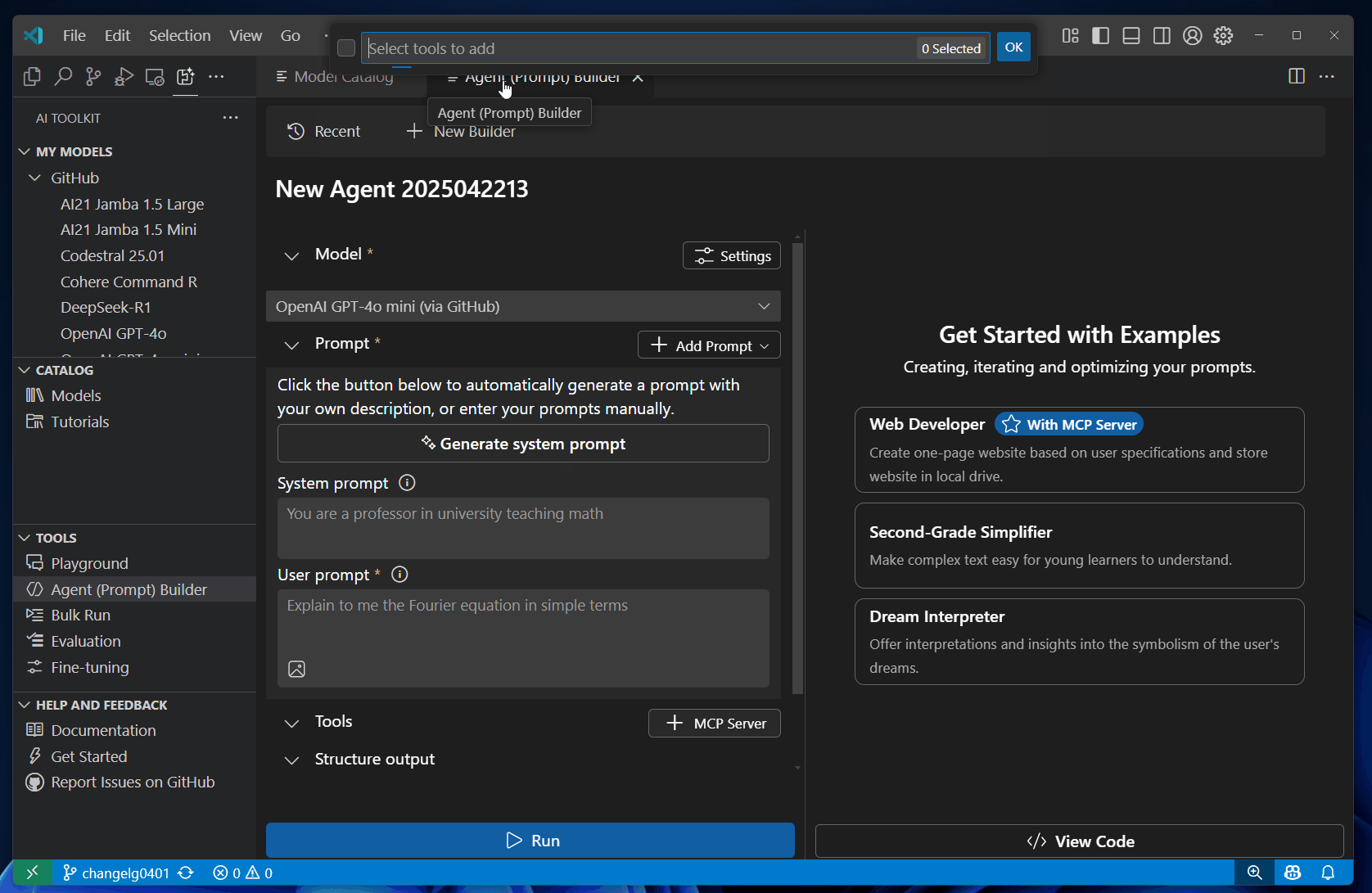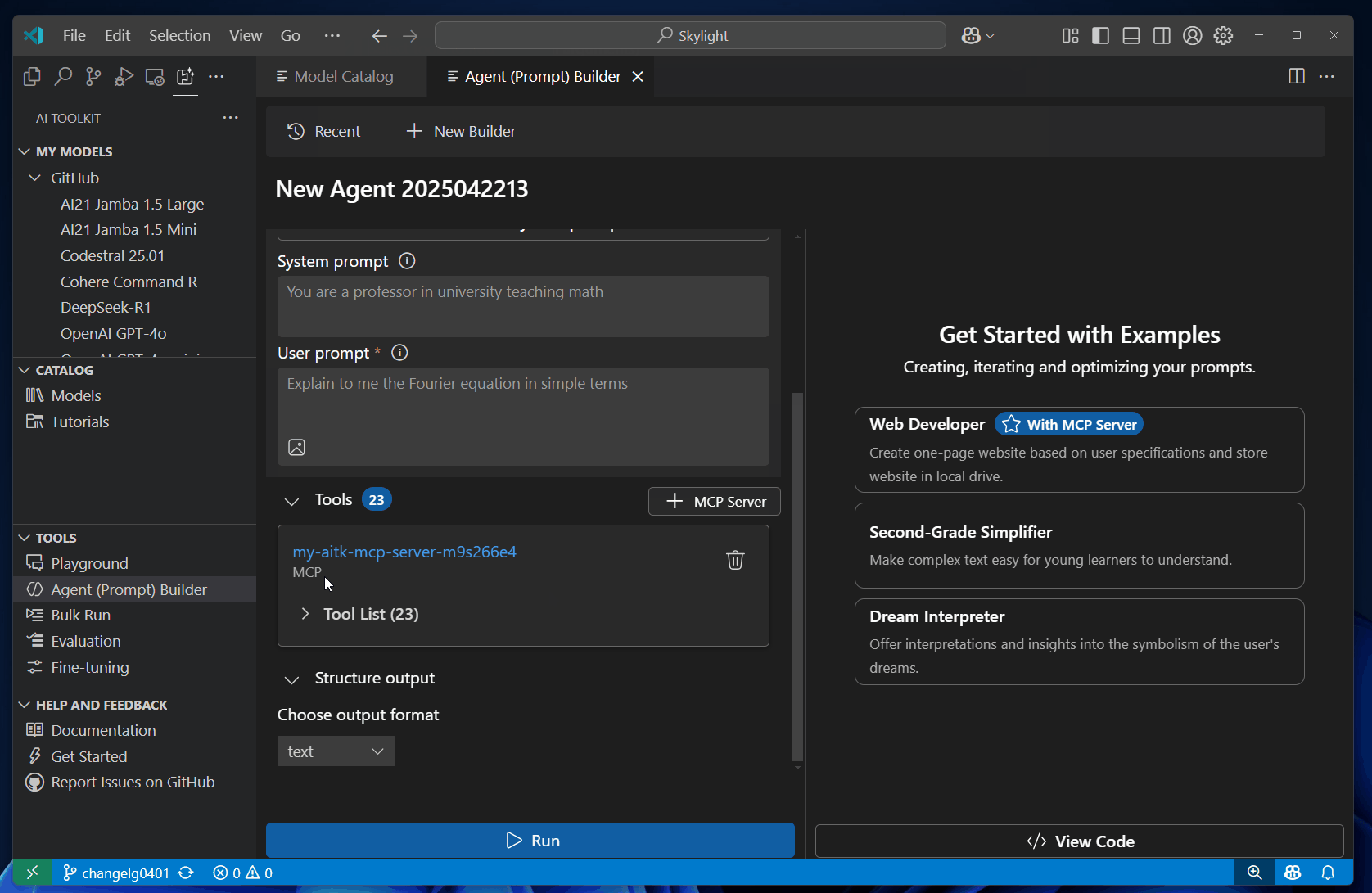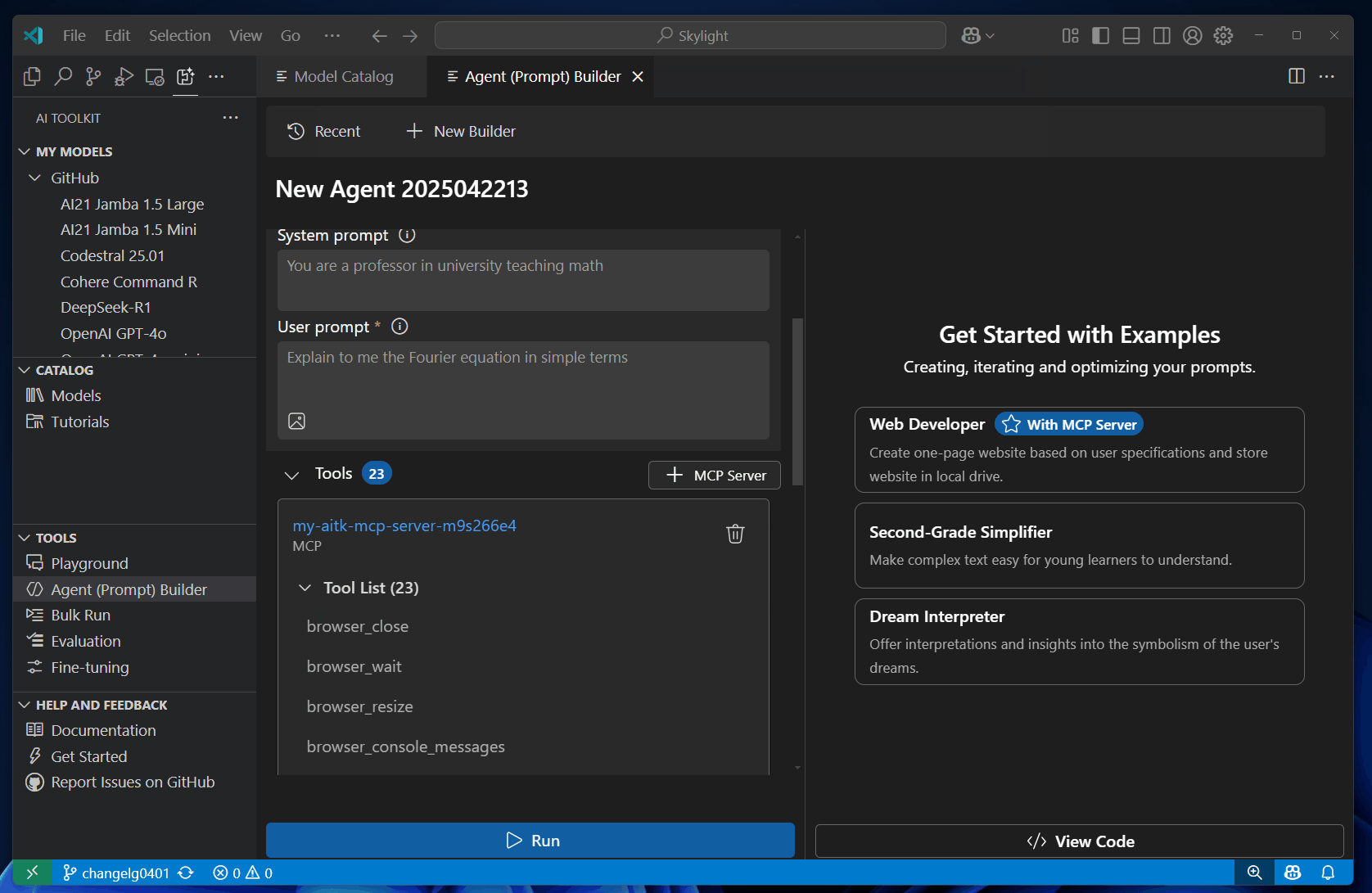
Select the tools you want to use.
AI Toolkit also provides a scaffold to help you build a new MCP server. The scaffold includes a basic implementation of the MCP protocol, which you can customize to suit your needs.
To build a new MCP server, follow these steps:
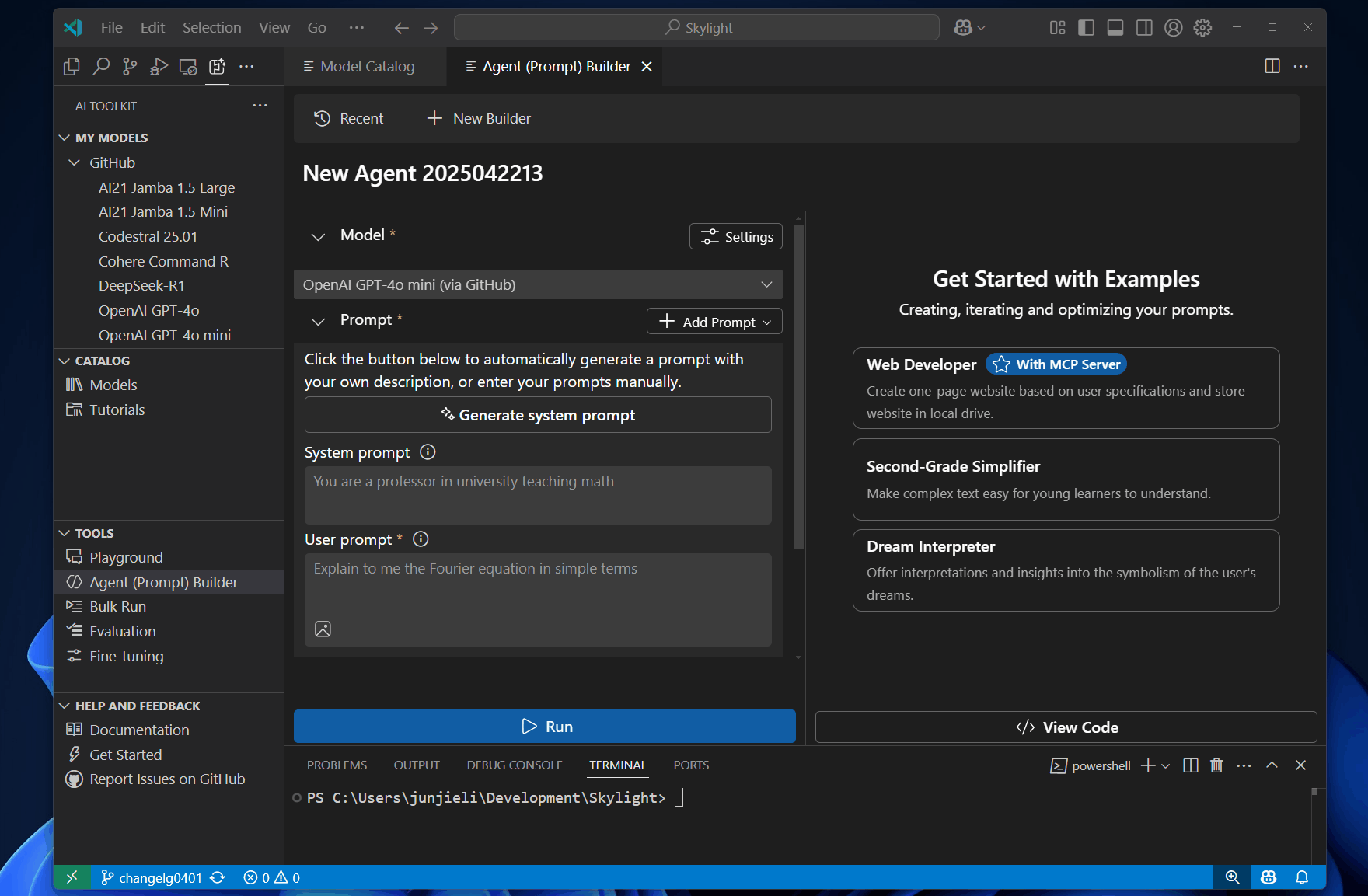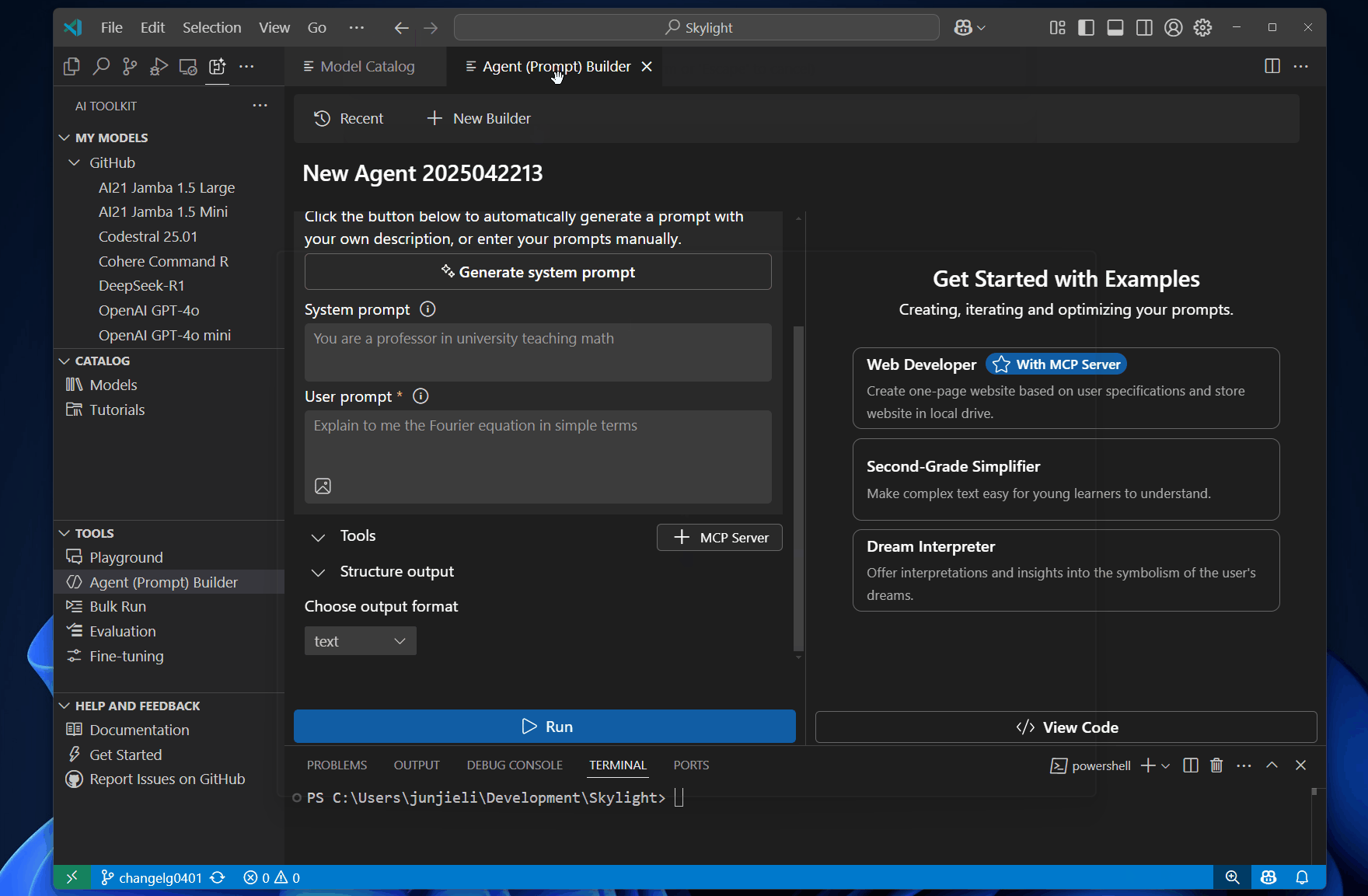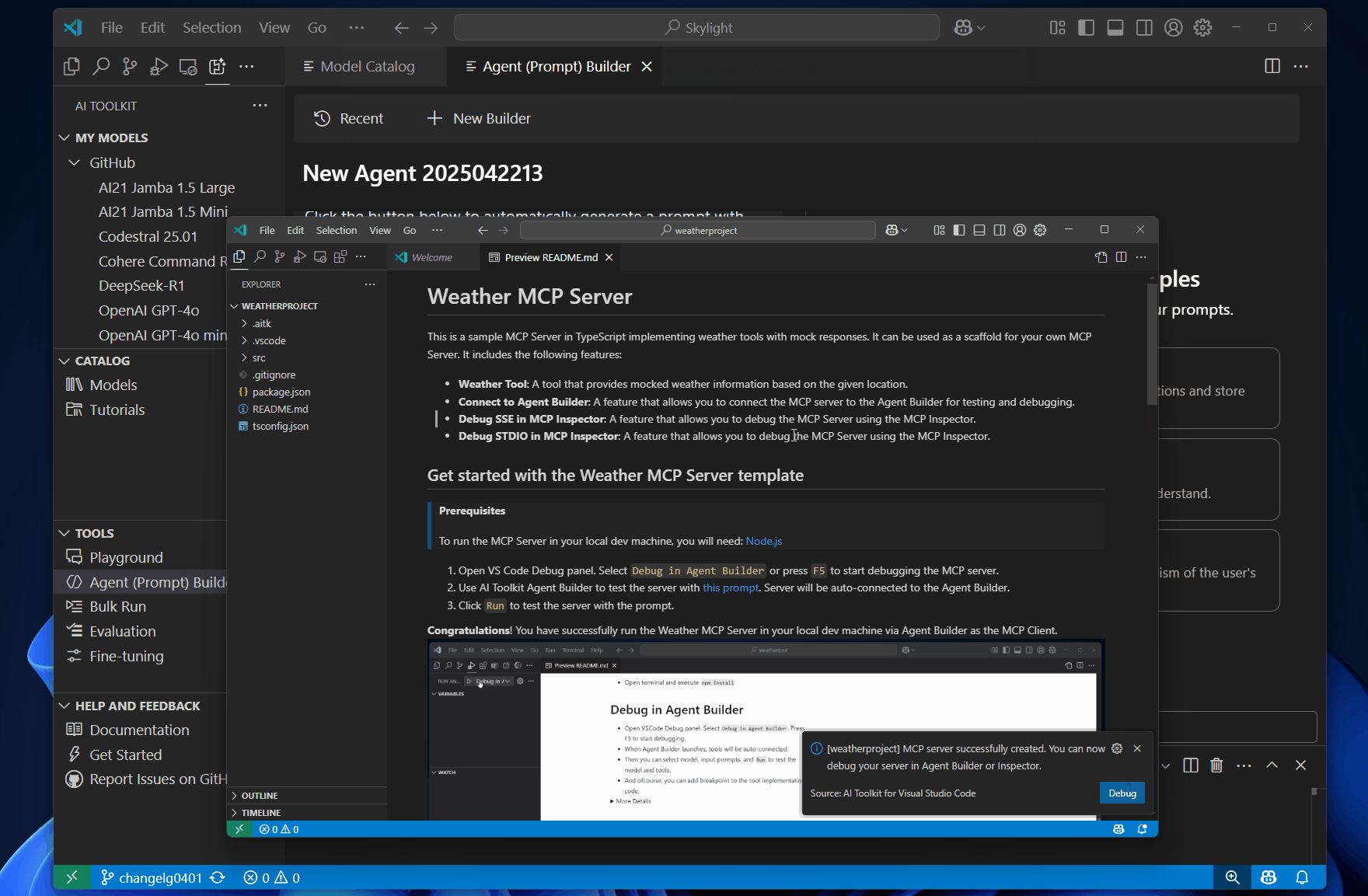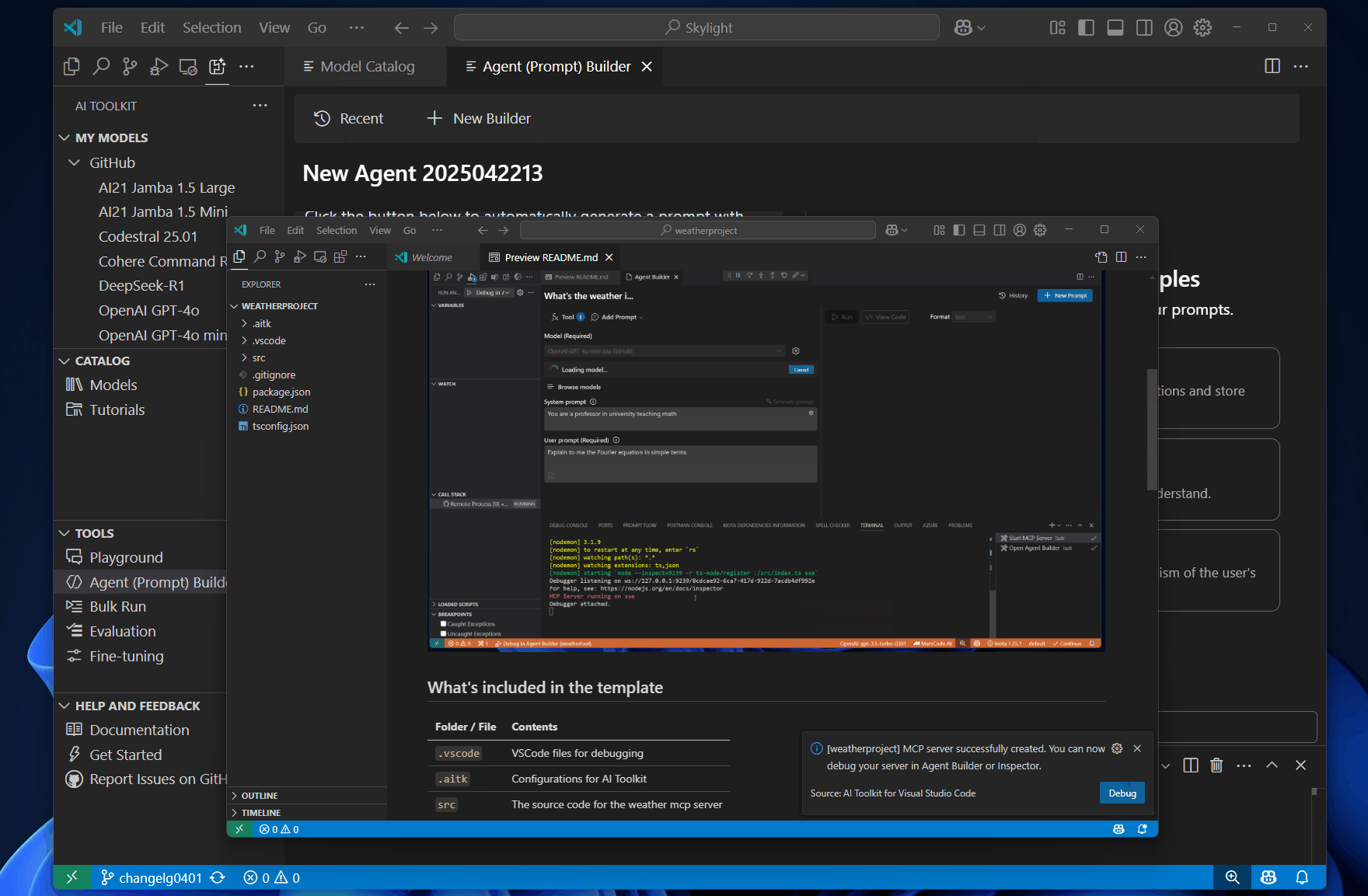
After you create the MCP server project, you can customize the implementation to suit your needs. The scaffold includes a basic implementation of the MCP protocol, which you can modify to add your own functionality.
You can also use the agent builder to test the MCP server. The agent builder sends the prompts to the MCP server and displays the response.
Follow these steps to test the MCP server:
To run the MCP Server in your local dev machine, you need: Node.js or Python installed on your machine.
Debug in Agent Builder or press F5 to start debugging the MCP server.Run to test the server with the prompt.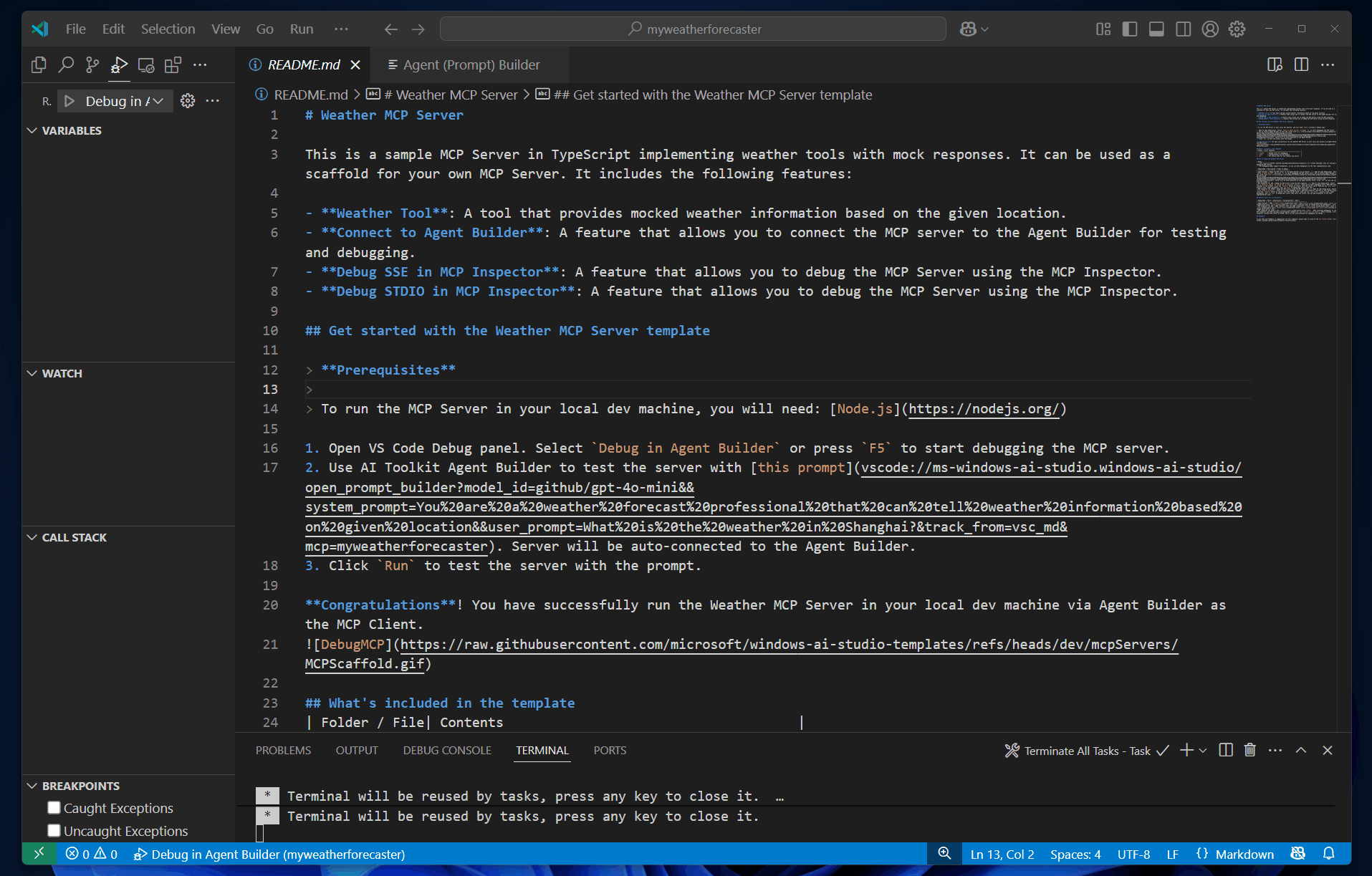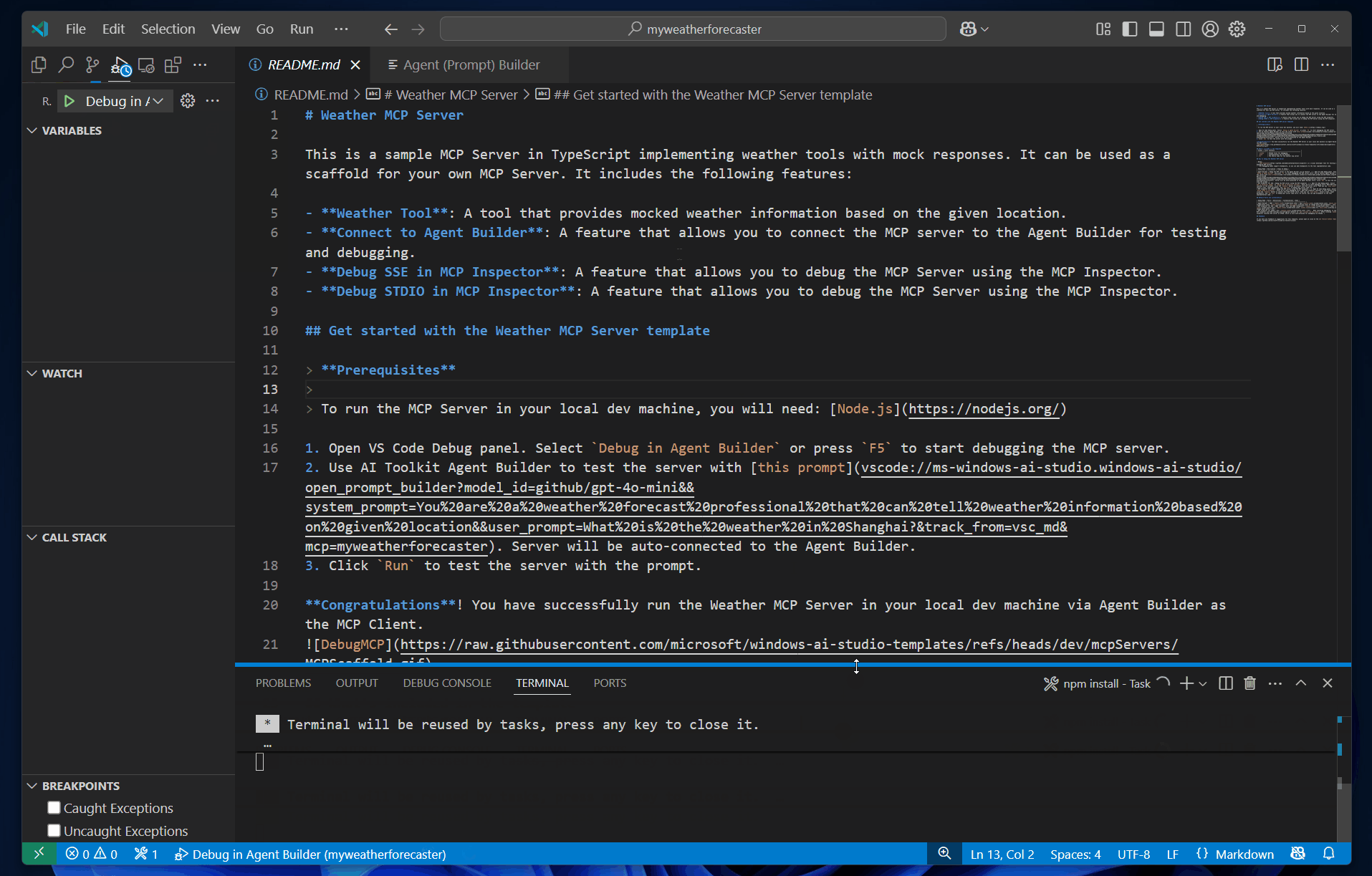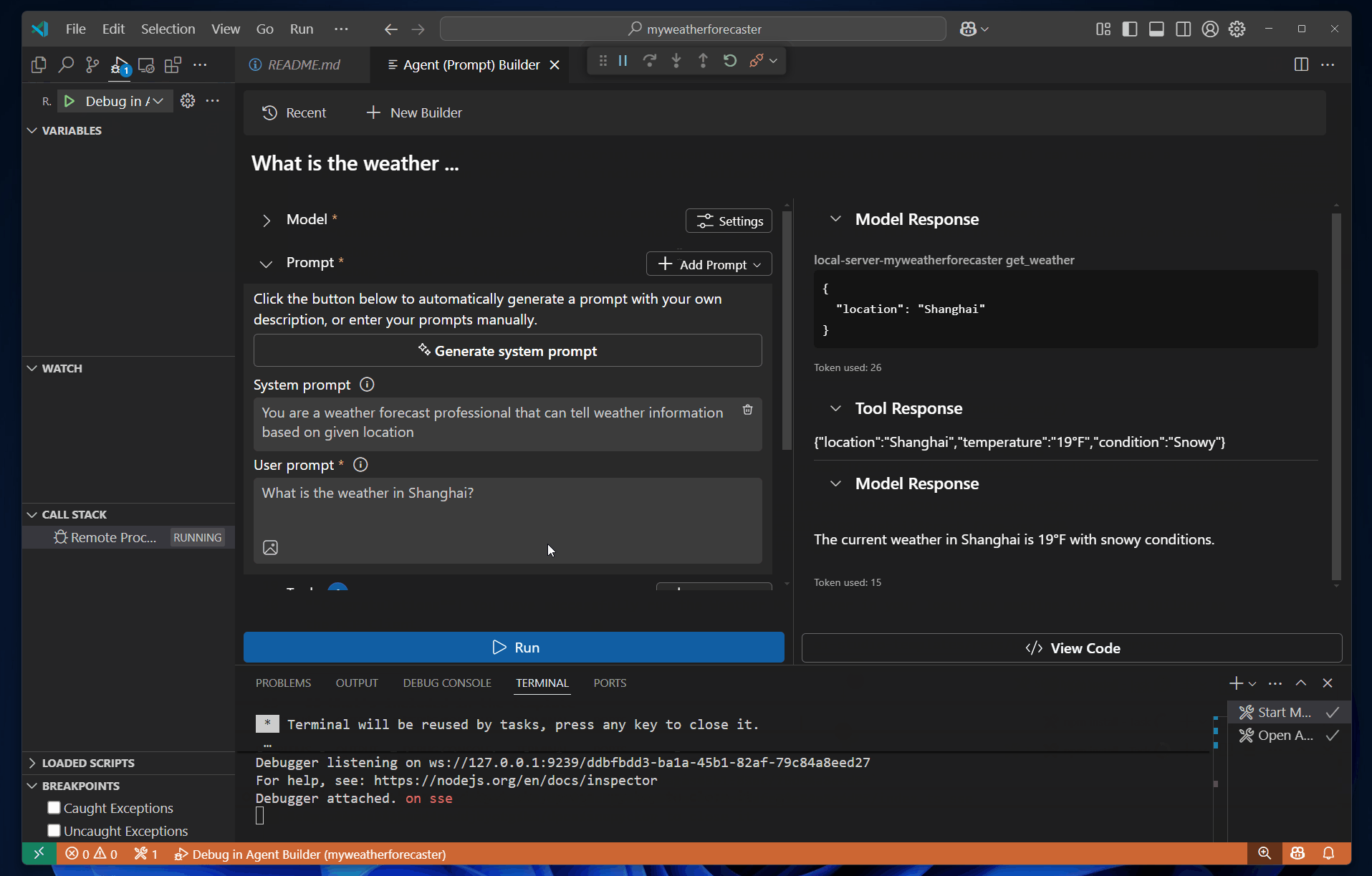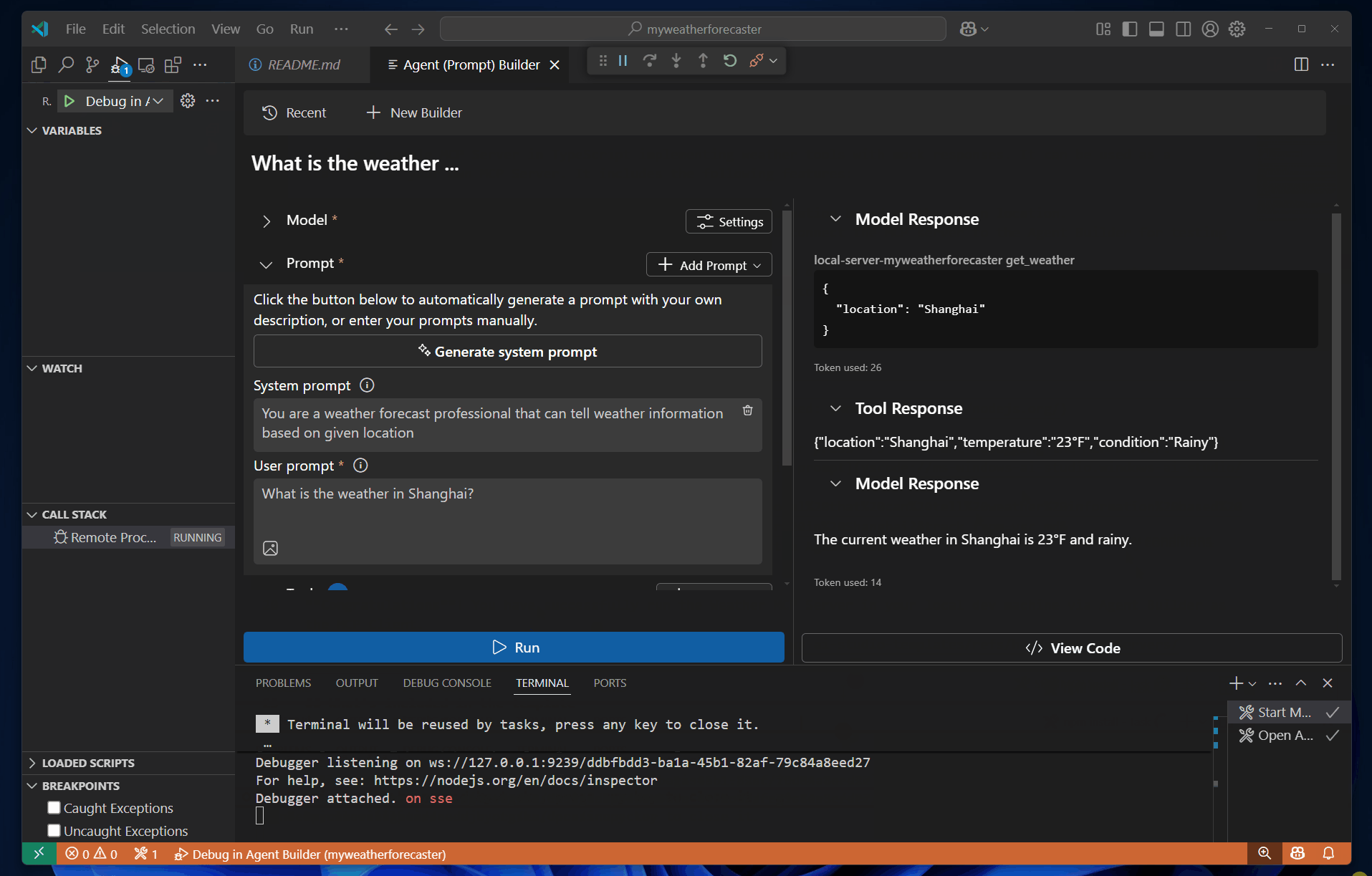
Function calling connects your agent to external APIs and services.
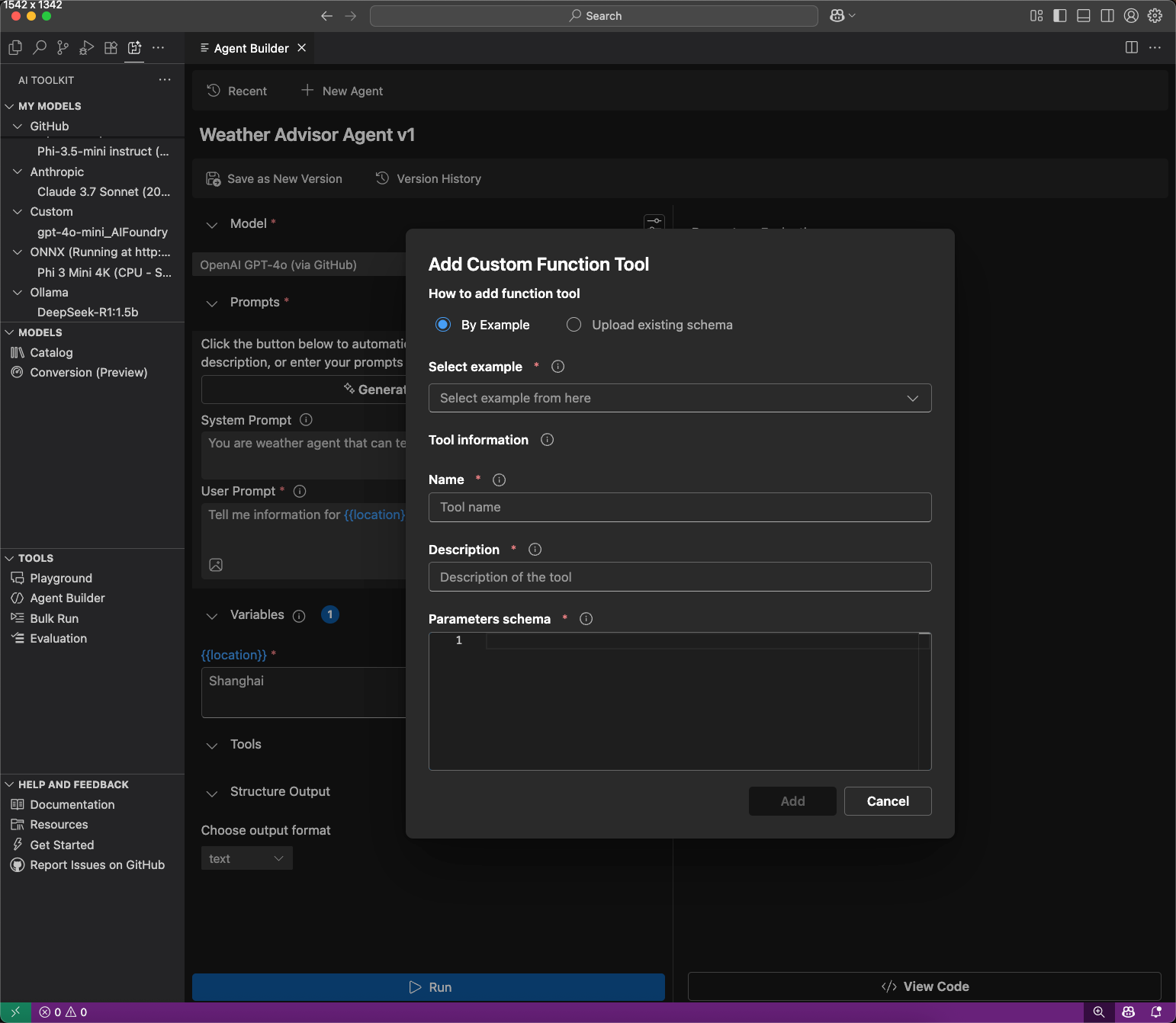
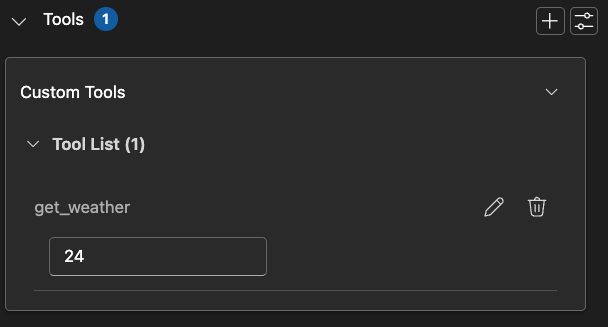
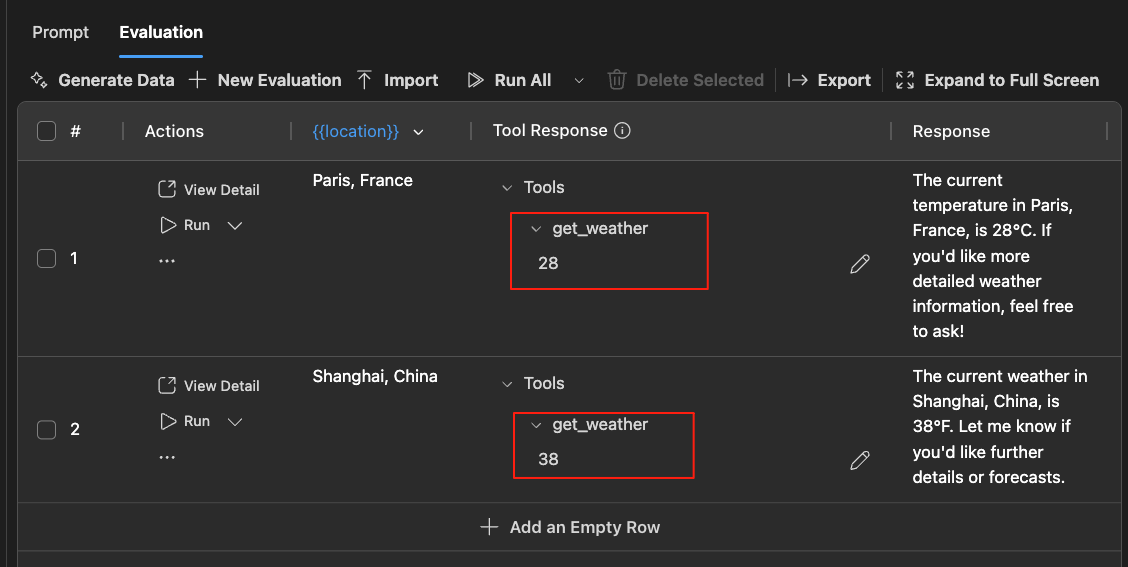
Use function calling tools in the Evaluation tab by entering mock responses for test cases.
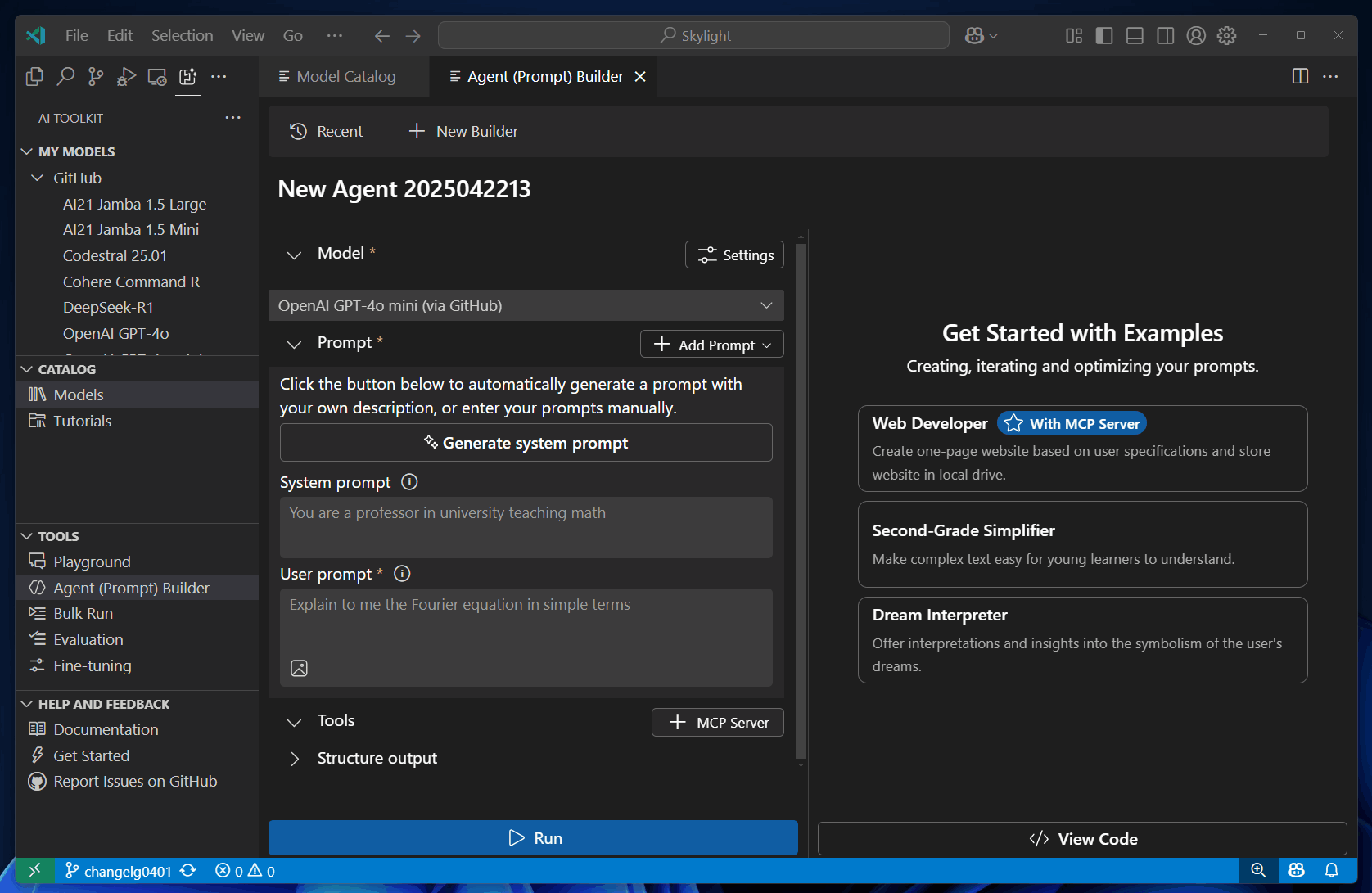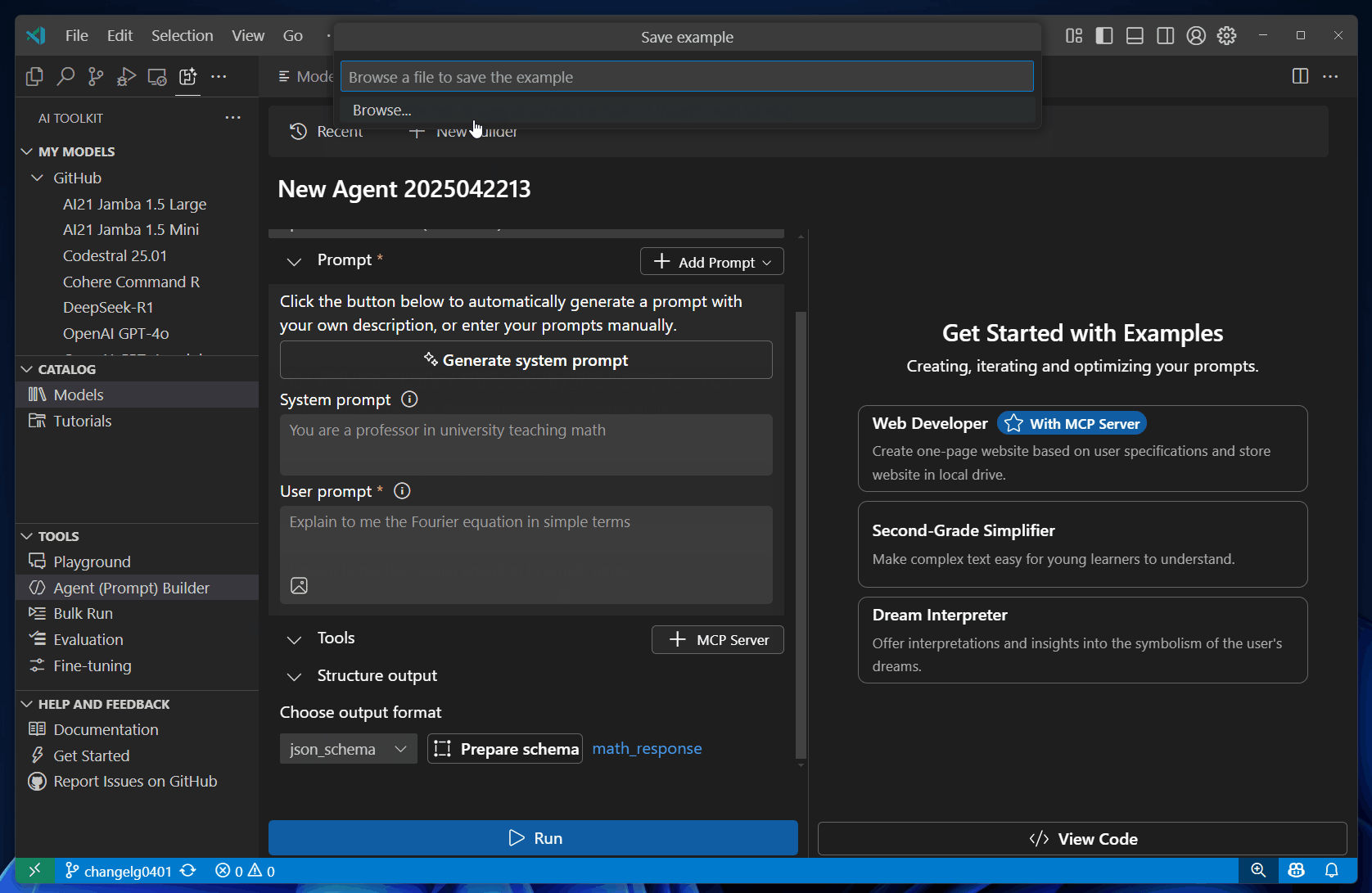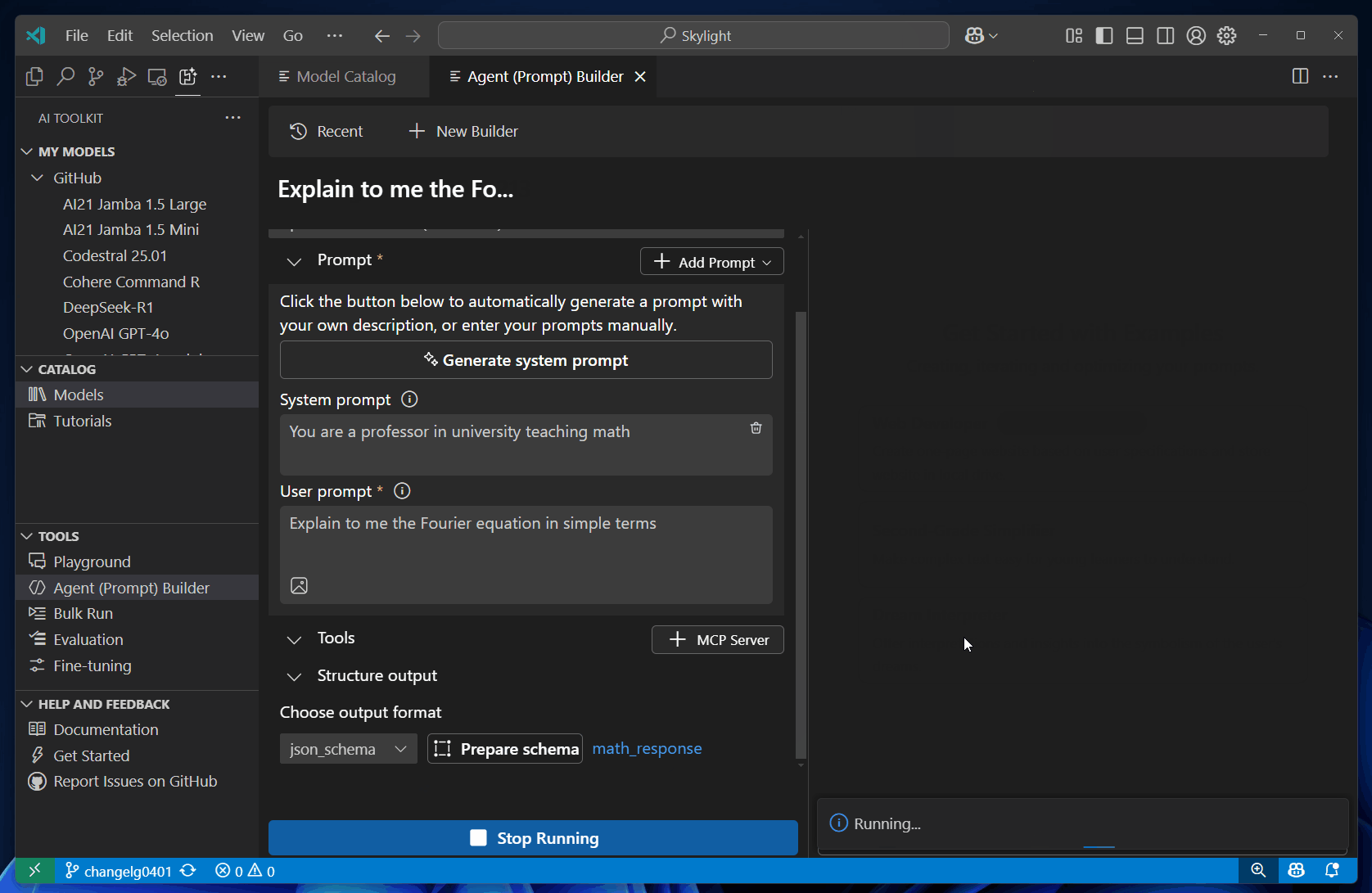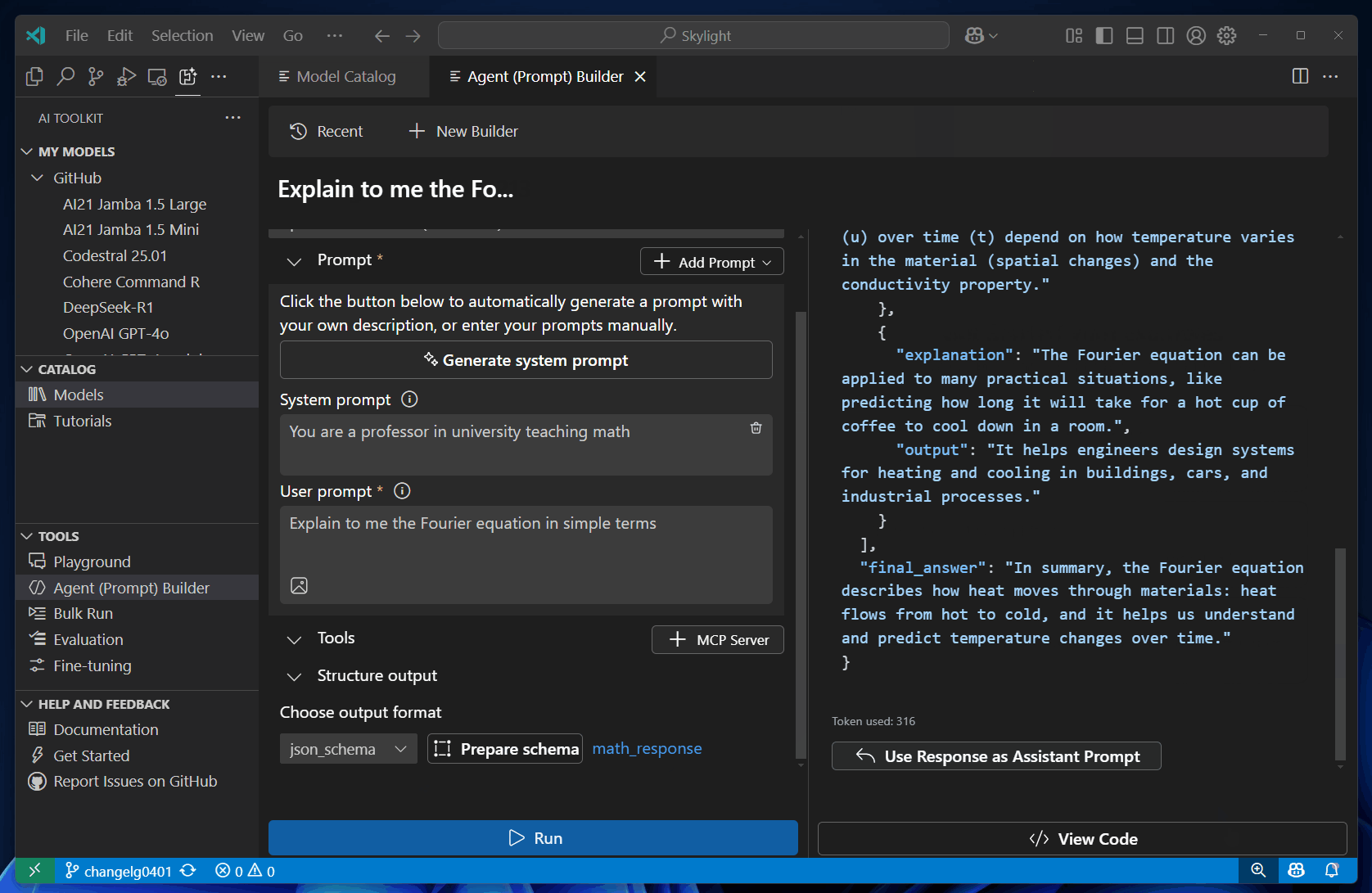
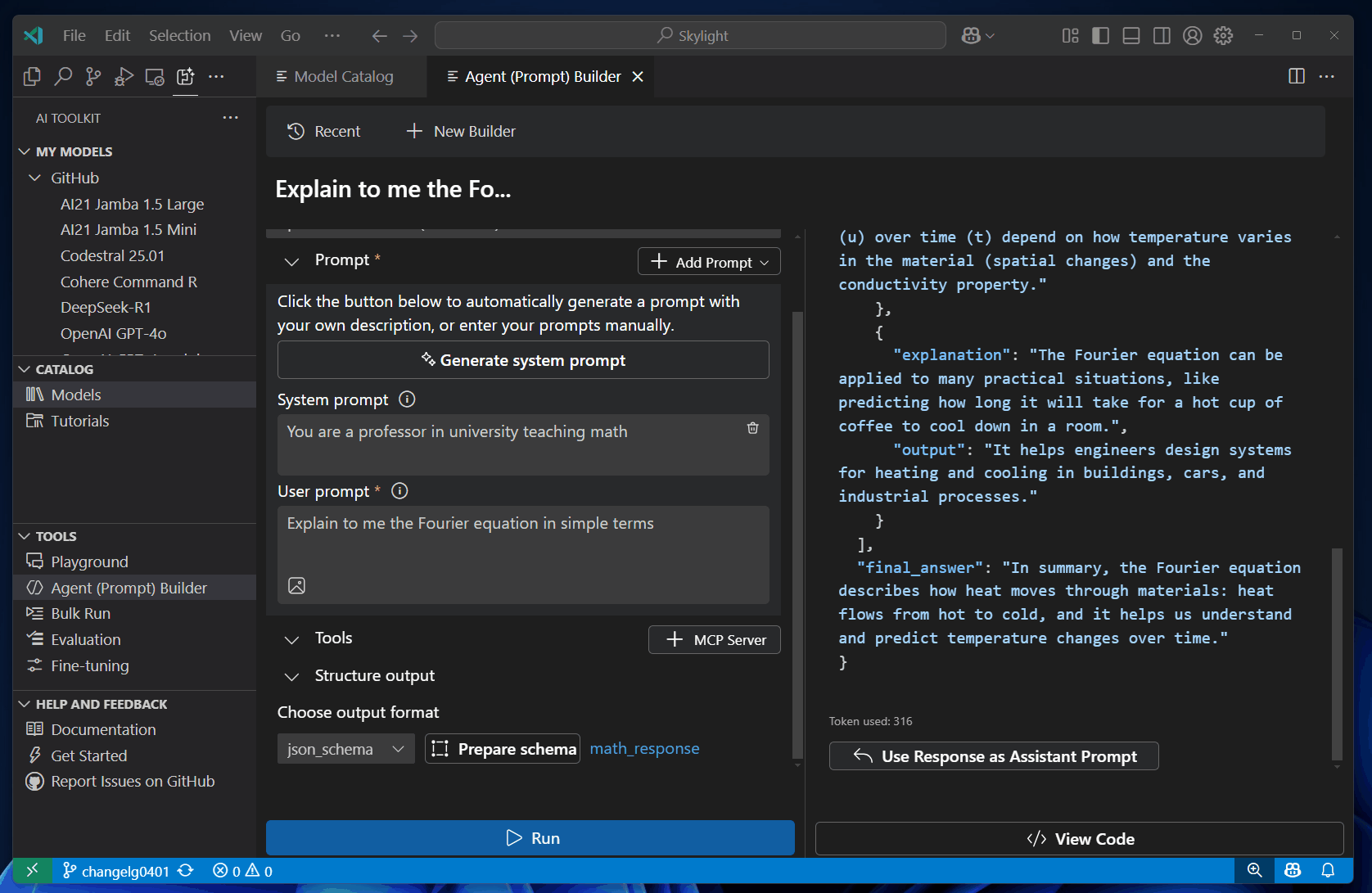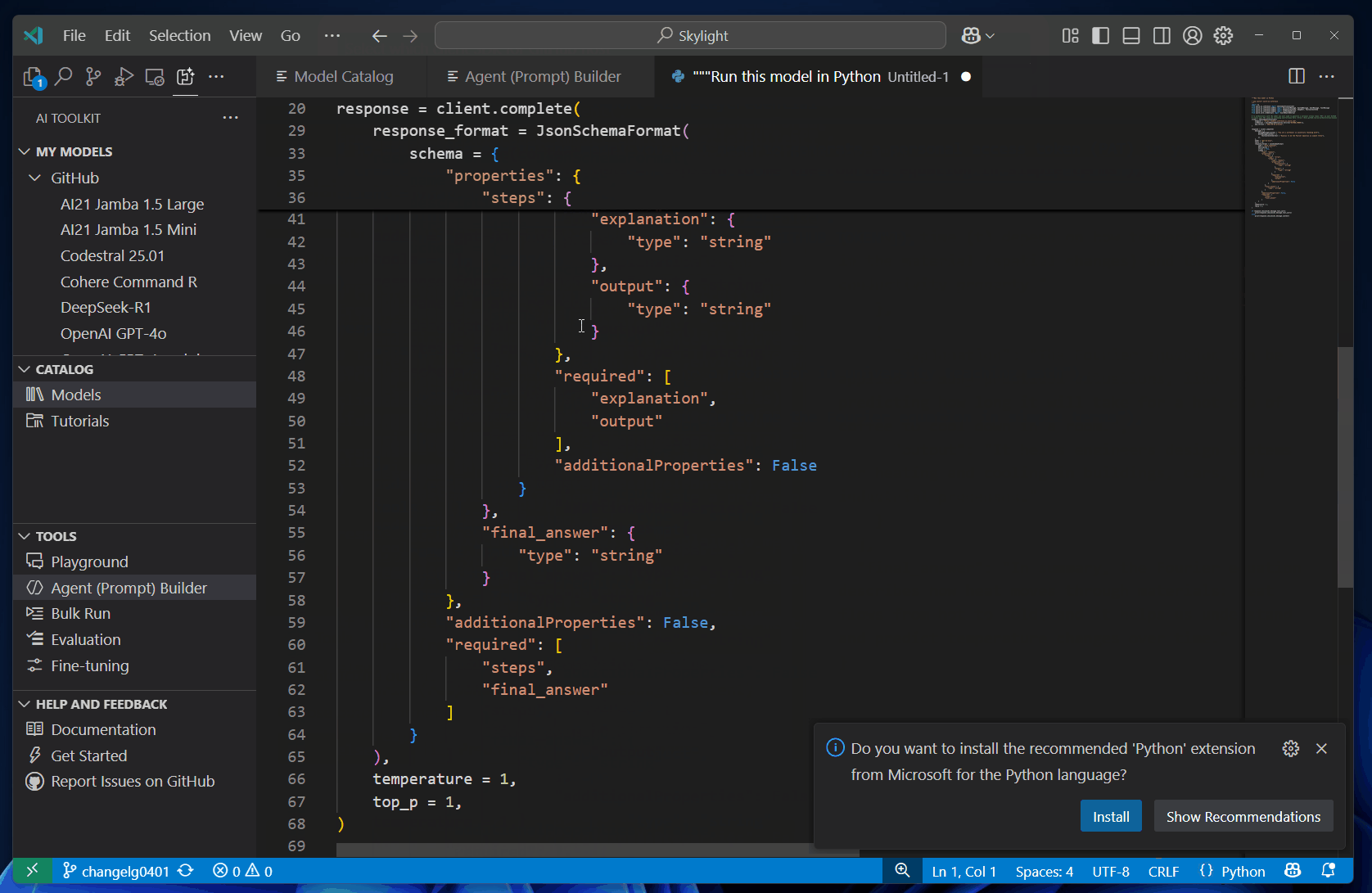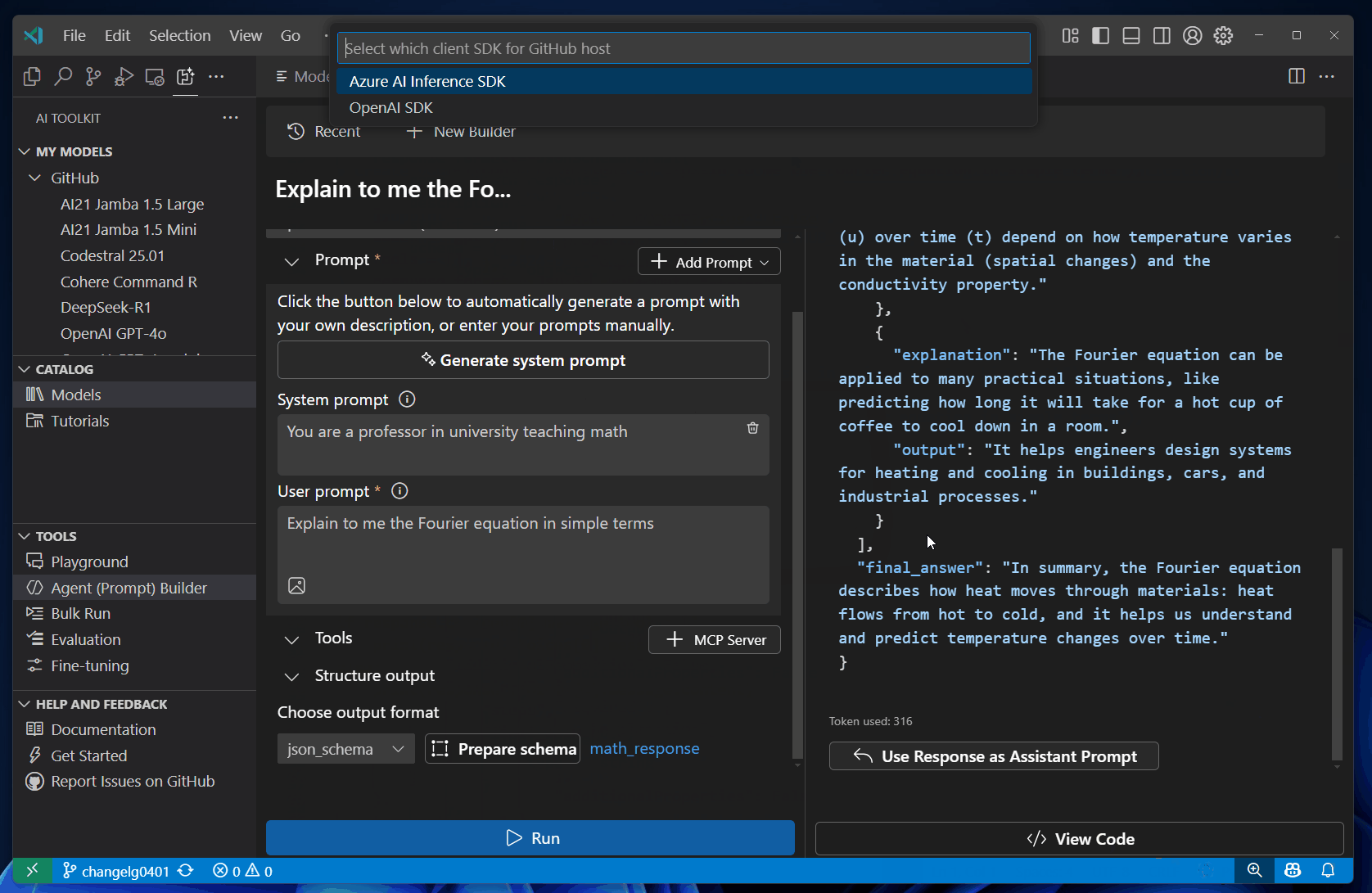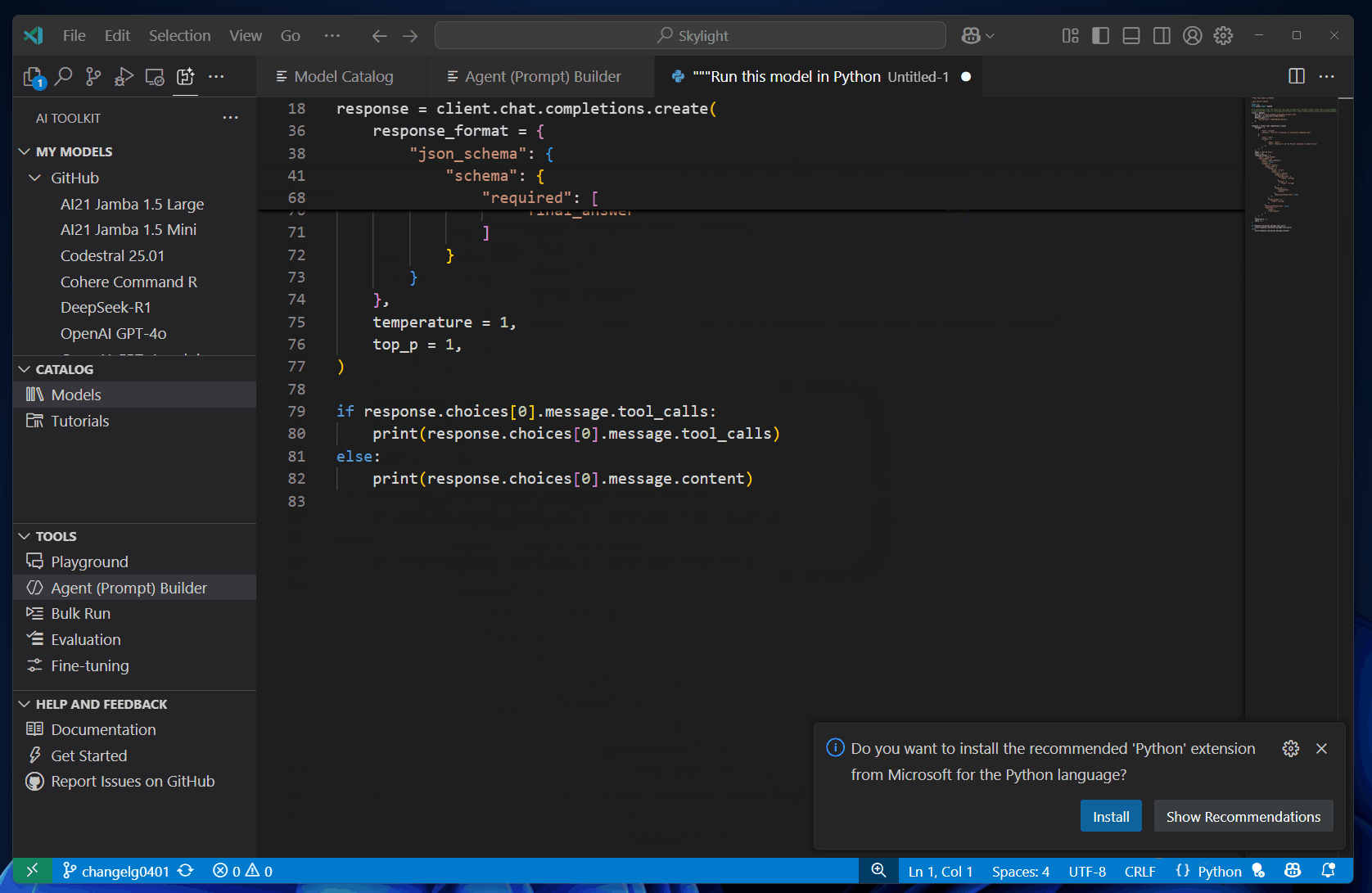
Structured output support helps you design prompts to deliver outputs in a structured, predictable format.
To test using structured output in Agent Builder, follow these steps:
Select the Structure output from the left area, and select json_schema.
Select Prepare schema, and then select Select local file to use your own schema, or select Use an example to use a predefined schema.
If you proceed with an example, you can select a schema from the dropdown list.
Select Run to send the prompts to the selected model.
You can also edit the schema by selecting name of the schema.
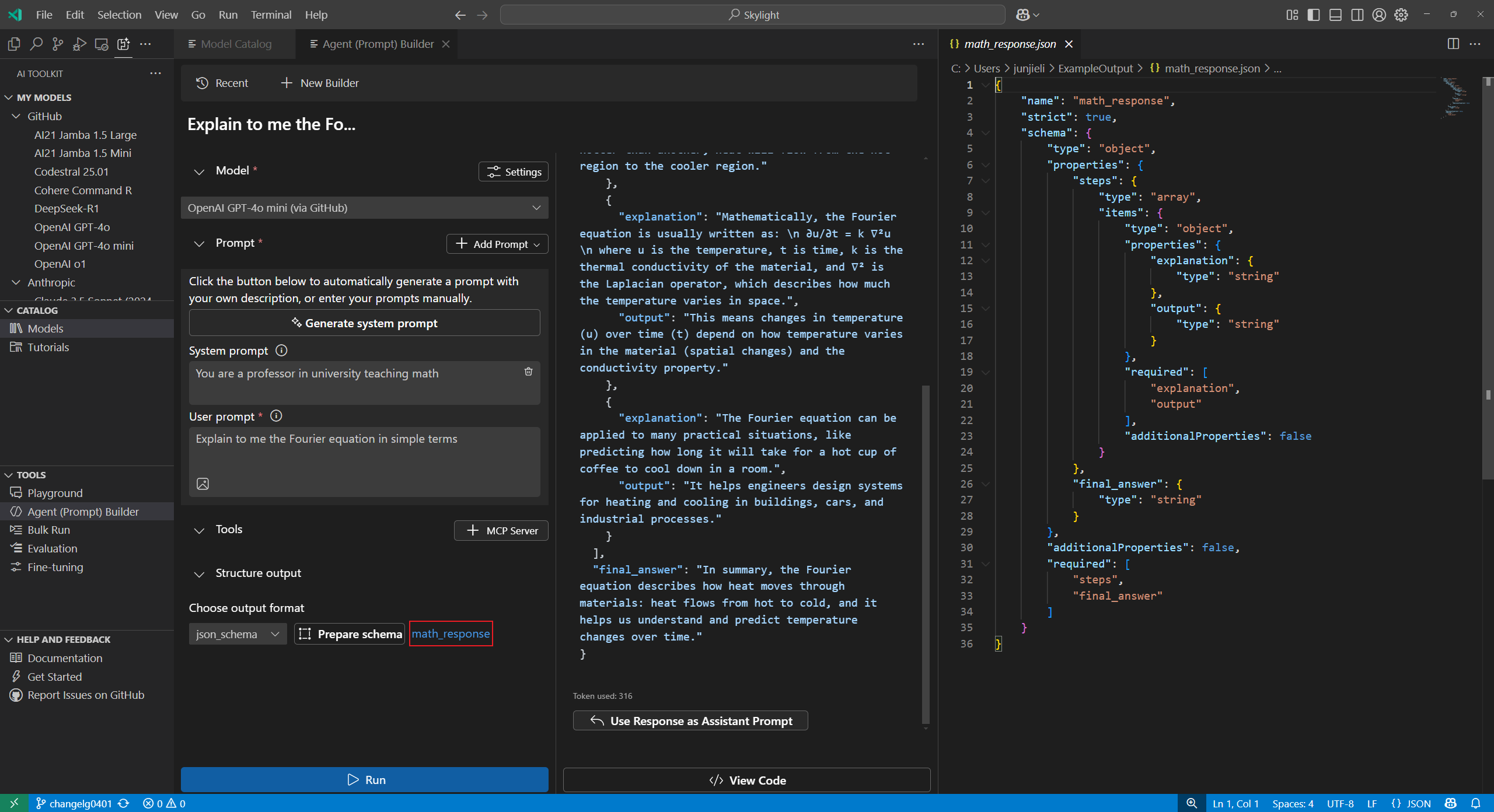
After experimenting with models and prompts, you can get into coding right away with the automatically generated Python code.
To view the Python code, follow these steps:
Select View Code.
For models hosted on GitHub, select the inference SDK you want to use.
AI Toolkit generates the code for the model you selected by using the provider's client SDK. For models hosted by GitHub, you can choose which inference SDK you want to use: Azure AI Inference SDK or the SDK from the model provider, such as OpenAI SDK or Mistral API.
The generated code snippet is shown in a new editor, where you can copy it into your application.
To authenticate with the model, you usually need an API key from the provider. To access models hosted by GitHub, generate a personal access token (PAT) in your GitHub settings.
In this article, you learned how to: